Assessment of ground-based atmospheric observations for verification of greenhouse gas emissions from an urban region
- PMID: 22611187
- PMCID: PMC3365165
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1116645109
Assessment of ground-based atmospheric observations for verification of greenhouse gas emissions from an urban region
Abstract
International agreements to limit greenhouse gas emissions require verification to ensure that they are effective and fair. Verification based on direct observation of atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations will be necessary to demonstrate that estimated emission reductions have been actualized in the atmosphere. Here we assess the capability of ground-based observations and a high-resolution (1.3 km) mesoscale atmospheric transport model to determine a change in greenhouse gas emissions over time from a metropolitan region. We test the method with observations from a network of CO(2) surface monitors in Salt Lake City. Many features of the CO(2) data were simulated with excellent fidelity, although data-model mismatches occurred on hourly timescales due to inadequate simulation of shallow circulations and the precise timing of boundary-layer stratification and destratification. Using two optimization procedures, monthly regional fluxes were constrained to sufficient precision to detect an increase or decrease in emissions of approximately 15% at the 95% confidence level. We argue that integrated column measurements of the urban dome of CO(2) from the ground and/or space are less sensitive than surface point measurements to the redistribution of emitted CO(2) by small-scale processes and thus may allow for more precise trend detection of emissions from urban regions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
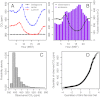

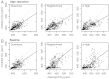
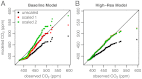

References
-
- Eggleston HS, Buendia L, Miwa K, Ngara T, Tanabe K, editors. Hayama, Japan: Inst for Global Environmental Strategies; 2006. 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. prepared by the National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Program.
-
- Committee on Methods for Estimating Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Washington, DC: Natl Acad Press; 2010. Verifying greenhouse gas emissions: method to support international climate agreements, National Research Council.
-
- Gregg JS, Andres RJ, Marland G. China: Emissions pattern of the world leader in CO2 emissions from fossil fuel consumption and cement production. Geophys Res Lett. 2008;35:L08806.
-
- Peylin P, et al. Importance of fossil fuel emission uncertainties over Europe for CO2 modeling: Model intercomparison. Atmos Chem Phys. 2011;11:6607–6622.
-
- Marland G. Uncertainties in accounting for CO2 from fossil fuels. J Ind Ecol. 2008;12:136–139.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

