Modeling and numerical simulation of blood flow using the Theory of Interacting Continua
- PMID: 22611284
- PMCID: PMC3352667
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnonlinmec.2011.09.025
Modeling and numerical simulation of blood flow using the Theory of Interacting Continua
Abstract
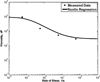
In this paper we use a modified form of the mixture theory developed by Massoudi and Rajagopal to study the blood flow in a simple geometry, namely flow between two plates. The blood is assumed to behave as a two-component mixture comprised of plasma and red blood cells (RBCs). The plasma is assumed to behave as a viscous fluid whereas the RBCs are given a granular-like structure where the viscosity also depends on the shear-rate.
Figures



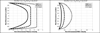


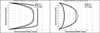















References
-
- Aarts P, Vandenbroek SAT, et al. Blood-platelets are concentrated near the wall and red blood-cells, in the center in flowing blood. Arteriosclerosis. 1988;8(6):819–824. - PubMed
-
- Adkins JE. Non-Linear Diffusion, 1. Diffusion and Flow of Mixtures of Fluids. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London A. 1963;255:607–633.
-
- Adkins JE. Non-Linear Diffusion, 2. Constitutive Equations for Mixtures of Isotropic Fluids. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London A. 1963;255:635–648.
-
- Anderson TB, Jackson R. A fluid mechanical description of fluidized beds. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals. 1967;6(4) 527-&.
-
- Araujo RP, Mcelwain DLS. A mixture theory for the genesis of residual stresses in growing tissues I. Siam Journal on Applied Mathematics. 2005;65 1261-
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
