Side-stream smoking reduces intestinal inflammation and increases expression of tight junction proteins
- PMID: 22611310
- PMCID: PMC3351767
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2180
Side-stream smoking reduces intestinal inflammation and increases expression of tight junction proteins
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of side-stream smoking on gut microflora composition, intestinal inflammation and expression of tight junction proteins.
Methods: C57BL/6 mice were exposed to side-stream cigarette smoking for one hour daily over eight weeks. Cecal contents were collected for microbial composition analysis. Large intestine was collected for immunoblotting and quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction analyses of the inflammatory pathway and tight junction proteins.
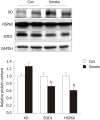
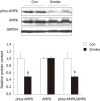
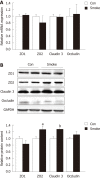
Results: Side-stream smoking induced significant changes in the gut microbiota with increased mouse intestinal bacteria, Clostridium but decreased Fermicutes (Lactoccoci and Ruminococcus), Enterobacteriaceae family and Segmented filamentous baceteria compared to the control mice. Meanwhile, side-stream smoking inhibited the nuclear factor-κB pathway with reduced phosphorylation of p65 and IκBα, accompanied with unchanged mRNA expression of tumor necrosis factor-α or interleukin-6. The contents of tight junction proteins, claudin3 and ZO2 were up-regulated in the large intestine of mice exposed side-stream smoking. In addition, side-stream smoking increased c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 MAPK kinase signaling, while inhibiting AMP-activated protein kinase in the large intestine.
Conclusion: Side-stream smoking altered gut microflora composition and reduced the inflammatory response, which was associated with increased expression of tight junction proteins.
Keywords: Inflammation; Intestine; Microbiota; Side-stream smoking; Tight junction protein.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Suppression of tumour necrosis factor-alpha by Schizonepeta tenuifolia water extract via inhibition of IkappaBalpha degradation and Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase activation.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010 Aug;62(8):1069-76. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.2010.01126.x. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20663042
-
Unexpected role of anticoagulant protein C in controlling epithelial barrier integrity and intestinal inflammation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Dec 6;108(49):19830-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1107140108. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 22109555 Free PMC article.
-
Total polysaccharides of the Sijunzi decoction attenuate tumor necrosis factor-α-induced damage to the barrier function of a Caco-2 cell monolayer via the nuclear factor-κB-myosin light chain kinase-myosin light chain pathway.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jul 14;24(26):2867-2877. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i26.2867. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30018481 Free PMC article.
-
Tight junctions on the move: molecular mechanisms for epithelial barrier regulation.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012 Jul;1258:9-18. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06613.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012. PMID: 22731710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Claudin Barriers on the Brink: How Conflicting Tissue and Cellular Priorities Drive IBD Pathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 10;24(10):8562. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108562. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239907 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Smoking-induced microbial dysbiosis in health and disease.Clin Sci (Lond). 2022 Sep 30;136(18):1371-1387. doi: 10.1042/CS20220175. Clin Sci (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36156126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary nicotine intake and risk of Parkinson disease: a prospective study.Am J Clin Nutr. 2020 Oct 1;112(4):1080-1087. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqaa186. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32725131 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Supplemental Calcium and Vitamin D on Expression of Toll-Like Receptors and Phospho-IKKα/β in the Normal Rectal Mucosa of Colorectal Adenoma Patients.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2018 Nov;11(11):707-716. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-18-0123. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2018. PMID: 30209117 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming Life: A Broad View of the Developmental Origins of Health and Disease Concept from an Ecological Justice Perspective.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016 Nov 3;13(11):1075. doi: 10.3390/ijerph13111075. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27827896 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary oregano essential oil supplementation improves intestinal functions and alters gut microbiota in late-phase laying hens.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2021 Jul 6;12(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s40104-021-00600-3. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34225796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singer MV, Feick P, Gerloff A. Alcohol and smoking. Dig Dis. 2011;29:177–183. - PubMed
-
- Frey P, Waters DD. Tobacco smoke and cardiovascular risk: a call for continued efforts to reduce exposure. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2011;26:424–428. - PubMed
-
- Birrenbach T, Bocker U. Inflammatory bowel disease and smoking: a review of epidemiology, pathophysiology, and therapeutic implications. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2004;10:848–859. - PubMed
-
- Virdis A, Giannarelli C, Neves MF, Taddei S, Ghiadoni L. Cigarette smoking and hypertension. Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16:2518–2525. - PubMed
-
- Ambrose JA, Barua RS. The pathophysiology of cigarette smoking and cardiovascular disease: an update. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:1731–1737. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

