Protective effects of 5-methoxypsoralen against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice
- PMID: 22611312
- PMCID: PMC3351769
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2197
Protective effects of 5-methoxypsoralen against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the hepatic protective effects of 5-methoxypsoralen (5-MOP) and to learn if 5-MOP causes hepatotoxicity at protective doses.
Methods: C57BL/6J mice were administrated orally with 5-MOP at doses of 12.5, 25 and 50 mg/kg body weight respectively every morning for 4 d before given acetaminophen (APAP) subcutaneously at a dose of 500 mg/kg. The 5-MOP alone group was treated with 5-MOP orally at a dose of 50 mg/kg body weight for 4 d without APAP. Twenty-four hours after APAP administration, blood samples of mice were analyzed for serum enzyme alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels, and malondialdehyde (MDA), reduced glutathione (GSH) and oxidized glutathione (GSSG) of liver tissues were measured and histopathologic changes of the liver were observed.
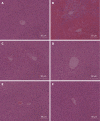
Results: Compared with the vehicle control group, the serum levels (IU/L) of ALT, AST and LDH were all increased significantly in APAP group (8355 ± 3940 vs 30 ± 21, P < 0.05; 6482 ± 4018 vs 146 ± 58, P < 0.05; 24627 ± 10975 vs 1504 ± 410, P < 0.05). Compared with APAP group, the serum ALT levels (IU/L) (1674 ± 1810 vs 8355 ± 3940, P < 0.05; 54 ± 39 vs 8355 ± 3940, P < 0.05; 19 ± 9 vs 8355 ± 3940, P < 0.05), AST levels (IU/L) (729 ± 685 vs 6482 ± 4108, P < 0.05; 187 ± 149 vs 6482 ± 4108, P < 0.05; 141 ± 12 vs 6482 ± 4108, P < 0.05) and LDH levels (IU/L) (7220 ± 6317 vs 24 627 ± 10 975, P < 0.05; 1618 ± 719 vs 24 627 ± 10 975, P < 0.05; 1394 ± 469 vs 24 627 ± 10 975, P < 0.05) were all decreased drastically in the three-dosage 5-MOP pretreatment groups. Pretreatment of 5-MOP could attenuate histopathologic changes induced by APAP, including hepatocellular necrosis and infiltration of inflammatory cells, and the effect was dose-dependent. MDA levels (nmol/mg) were decreased by 5-MOP in a dose-dependent manner (0.98 ± 0.45 vs 2.15 ± 1.07, P > 0.05; 0.59 ± 0.07 vs 2.15 ± 1.07, P < 0.05; 0.47 ± 0.06 vs 2.15 ± 1.07, P < 0.05). The pretreatment of 5-MOP could also increase the GSH/GSSG ratio (3.834 ± 0.340 vs 3.306 ± 0.282, P > 0.05; 5.330 ± 0.421 vs 3.306 ± 0.282, P < 0.05; 6.180 ± 0.212 vs 3.306 ± 0.282, P < 0.05). In the group treated with 5-MOP but without APAP, the serum enzyme levels, the liver histopathologic manifestation, and the values of MDA and GSH/GSSG ratio were all normal.
Conclusion: 5-MOP can effectively protect C57BL/6J mice from APAP-induced hepatotoxicity and possesses an antioxidative activity, and does not cause liver injury at the protective doses.
Keywords: 5-Methoxypsoralen; Acetaminophen; Antioxidation; Hepatotoxicity; Protection.
Figures
References
-
- Larson AM, Polson J, Fontana RJ, Davern TJ, Lalani E, Hynan LS, Reisch JS, Schiødt FV, Ostapowicz G, Shakil AO, et al. Acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure: results of a United States multicenter, prospective study. Hepatology. 2005;42:1364–1372. - PubMed
-
- Murray KF, Hadzic N, Wirth S, Bassett M, Kelly D. Drug-related hepatotoxicity and acute liver failure. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008;47:395–405. - PubMed
-
- Norris W, Paredes AH, Lewis JH. Drug-induced liver injury in 2007. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2008;24:287–297. - PubMed
-
- Craig DG, Ford AC, Hayes PC, Simpson KJ. Systematic review: prognostic tests of paracetamol-induced acute liver failure. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;31:1064–1076. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

