Chitosan-hyaluronate hybrid gel intraarticular injection delays osteoarthritis progression and reduces pain in a rat meniscectomy model as compared to saline and hyaluronate treatment
- PMID: 22611500
- PMCID: PMC3352251
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/979152
Chitosan-hyaluronate hybrid gel intraarticular injection delays osteoarthritis progression and reduces pain in a rat meniscectomy model as compared to saline and hyaluronate treatment
Abstract
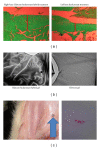
Chitosan-Hyaluronate hybrid gel (CHHG) is a self-forming thermo-responsive hydrogel. The current study was undertaken in order to assess the effect of CHHG on rat's surgically induced osteoarthritis. Methods. Thirteen rats were included in the study. In all rats weight-bearing was assessed using a Linton Incapacitance tester. All rats underwent bilateral medial partial meniscectomy. Four rats received a saline injection in the control knee and a 200-microliter injection of CHHG in the experimental knee. Five rats received a high-molecular weight hyaluronate injection to the control knee and a 200-microliter injection of CHHG in the experimental knee. Four rats underwent the same surgical procedure, allowed to recuperate for seven days and then CHHG and hyaluronate were injected. The animals were followed for 6 weeks. Two weeks after injection of a therapeutic substance the amount of weight-bearing on each knee was evaluated using a Linton Incapacitance meter. Results. Two weeks after induction of osteoarthritis there is less pain in the CHHG-treated knee than in the control-treated knee, as determined using a Lintron Incapacitance meter. After six-weeks the histological appearance of the CHHG-treated knee was superior to that of the controls. This is indicated by thicker cartilage remaining on the medial femoral condyle as well as less cyst formation in the CHHG-treated knee. Discussion. CHHG appears to delay progression of osteoarthritis and lessen pain in a rat surgically-induced knee osteoarthritis model. These results support other published results, indicating that there is an ameliorative effect of chitosan on human and rabbit osteoarthritis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acupotomy versus sodium hyaluronate for treatment of knee osteoarthritis in rabbits.J Tradit Chin Med. 2017 Jun;37(3):404-411. J Tradit Chin Med. 2017. PMID: 31682385
-
Efficacy and safety of intraarticular sodium hyaluronate in knee osteoarthritis. ORTHOVISC Study Group.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001 Apr;(385):130-43. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200104000-00021. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001. PMID: 11302304 Clinical Trial.
-
Pilot Study to Evaluate the Efficacy of Polynucleotide Sodium Compared to Sodium Hyaluronate and Crosslinked Sodium Hyaluronate in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis.J Clin Med. 2021 Mar 9;10(5):1138. doi: 10.3390/jcm10051138. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33803080 Free PMC article.
-
Chondroprotective effect of N-acetylglucosamine and hyaluronate in early stages of osteoarthritis--an experimental study in rabbits.Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2009;67(4):352-7. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2009. PMID: 20001938
-
Subgroups of patients with osteoarthritis and medial meniscus tear or crystal arthropathy benefit from arthroscopic treatment.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019 Mar;27(3):782-796. doi: 10.1007/s00167-018-5086-0. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019. PMID: 30128683
Cited by
-
Chitosan in viscosupplementation: in vivo effect on rabbit subchondral bone.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017 Aug 15;18(1):350. doi: 10.1186/s12891-017-1700-4. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017. PMID: 28810851 Free PMC article.
-
Versatile Use of Chitosan and Hyaluronan in Medicine.Molecules. 2021 Feb 23;26(4):1195. doi: 10.3390/molecules26041195. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33672365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Active agents, biomaterials, and technologies to improve biolubrication and strengthen soft tissues.Biomaterials. 2018 Oct;181:210-226. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.07.040. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Biomaterials. 2018. PMID: 30092370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intra-articular Injection of Chitosan-Based Supramolecular Hydrogel for Osteoarthritis Treatment.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021 Feb;18(1):113-125. doi: 10.1007/s13770-020-00322-z. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021. PMID: 33511556 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Chitosan Deacetylation on Its Affinity to Type III Collagen: A Molecular Dynamics Study.Materials (Basel). 2022 Jan 8;15(2):463. doi: 10.3390/ma15020463. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35057179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Song J, Suh CH, Park YB, et al. A phase I/IIa study on intra-articular injection of holmium-166-chitosan complex for the treatment of knee synovitis of rheumatoid arthritis. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 2001;28(4):489–497. - PubMed
-
- Malette WG, Quigley HJ, Gaines RD. Chitosan: a new hemostatic. Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 1983;36(1):55–58. - PubMed
-
- Minami S, Okamoto Y, Hamada K, Fukumoto Y, Shigemasa Y. Veterinary practice with chitin and chitosan. EXS. 1999;87:265–277. - PubMed
-
- Hombach J, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Chitosan solutions and particles: evaluation of their permeation enhancing potential on MDCK cells used as blood brain barrier model. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2009;376(1-2):104–109. - PubMed
-
- Cho BC, Park JW, Baik BS, Kwon IC, Kim IS. The role of hyaluronic acid, chitosan, and calcium sulfate and their combined effect on early bony consolidation in distraction osteogenesis of a canine model. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery. 2002;13(6):783–793. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

