Mesalamine-induced myocarditis and coronary vasculitis in a pediatric ulcerative colitis patient: a case report
- PMID: 22611512
- PMCID: PMC3350175
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/524364
Mesalamine-induced myocarditis and coronary vasculitis in a pediatric ulcerative colitis patient: a case report
Abstract
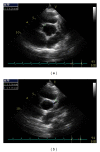
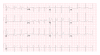
Mesalamine-containing products are often a first-line treatment for ulcerative colitis. Severe adverse reactions to these products, including cardiovascular toxicity, are rarely seen in pediatric patients. We present a case of a 16-year-old boy with ulcerative colitis treated with Asacol, a mesalamine-containing product, who developed sudden onset chest pain after four weeks on therapy. Serial electrocardiograms showed nonspecific ST segment changes, an echocardiogram showed mildly decreased left ventricular systolic function with mild to moderate left ventricular dilation and coronary ectasia, and his troponins were elevated. Following Asacol discontinuation, his chest pain resolved, troponins were trending towards normal, left ventricular systolic function normalized, and coronary ectasia improved within 24 hours suggesting an Asacol-associated severe drug reaction. Mesalamine-induced cardiovascular toxicity, although rare, may represent a life-threatening disorder. Therefore, every patient presenting with acute chest pain should receive a workup to rule out this rare drug-induced disorder.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Severe chest pain in a pediatric ulcerative colitis patient after 5-aminosalicylic acid therapy.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Jul 21;14(27):4400-2. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4400. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18666333 Free PMC article.
-
Mesalamine-induced myocarditis following diagnosis of Crohn's disease: a case report.Rev Port Cardiol. 2013 Sep;32(9):717-20. doi: 10.1016/j.repc.2012.12.018. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Rev Port Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23993290
-
Delayed-release oral mesalamine at 4.8 g/day (800 mg tablet) for the treatment of moderately active ulcerative colitis: the ASCEND II trial.Am J Gastroenterol. 2005 Nov;100(11):2478-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.00248.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16279903 Clinical Trial.
-
Mesalamine and olsalazine: 5-aminosalicylic acid agents for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease.Clin Pharm. 1992 Jun;11(6):514-28. Clin Pharm. 1992. PMID: 1600685 Review.
-
Mesalamine in the Initial Therapy of Ulcerative Colitis.Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2020 Dec;49(4):689-704. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2020.07.002. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2020. PMID: 33121689 Review.
Cited by
-
Urinary manifestations in African American and Caucasian inflammatory bowel disease patients: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Urol. 2022 Jan 4;22(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12894-021-00951-z. BMC Urol. 2022. PMID: 34983468 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Xanthan Gum-Based Oral Drug Delivery Systems.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 21;25(18):10143. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810143. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of clinical characteristics of mesalazine-induced cardiotoxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 15;13:970597. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.970597. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36188558 Free PMC article.
-
Myocarditis Related to the Use of Mesalazine.J Med Cases. 2023 Jul;14(7):237-243. doi: 10.14740/jmc4104. Epub 2023 Jul 31. J Med Cases. 2023. PMID: 37560552 Free PMC article.
-
Mesalamine-induced Myocarditis in a Young Athlete: Can He Run Again?Cureus. 2019 Jan 29;11(1):e3978. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3978. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 30967978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scribano ML. Adverses effects of IBD therapies. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2008;14(S2):210–211. - PubMed
-
- Loftus EV, Jr., Kane SV, Bjorkman D. Systematic review: short-term adverse effects of 5-aminosalicylic acid agents in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2004;19(2):179–189. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Ferrer L, Estornell J, Palanca V. Myocarditis by mesalazine with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. European Heart Journal. 2009;30(8):p. 1015. - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa N, Imamura T, Nakajima K, et al. Acute pericarditis associated with 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) treatment for severe active ulcerative colitis. Internal Medicine. 2001;40(9):901–904. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

