The melanosomal protein PMEL17 as a target for antibody drug conjugate therapy in melanoma
- PMID: 22613716
- PMCID: PMC3397835
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.361485
The melanosomal protein PMEL17 as a target for antibody drug conjugate therapy in melanoma
Abstract
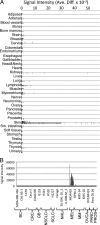
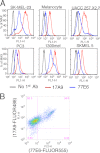
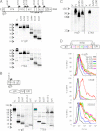
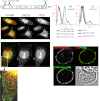
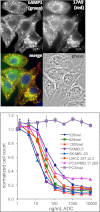
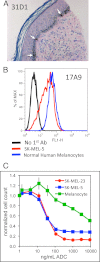
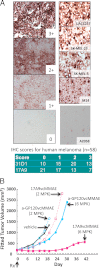
Melanocytes uniquely express specialized genes required for pigment formation, some of which are maintained following their transformation to melanoma. Here we exploit this property to selectively target melanoma with an antibody drug conjugate (ADC) specific to PMEL17, the product of the SILV pigment-forming gene. We describe new PMEL17 antibodies that detect the endogenous protein. These antibodies help define the secretory fate of PMEL17 and demonstrate its utility as an ADC target. Although newly synthesized PMEL17 is ultimately routed to the melanosome, we find substantial amounts accessible to our antibodies at the cell surface that undergo internalization and routing to a LAMP1-enriched, lysosome-related organelle. Accordingly, an ADC reactive with PMEL17 exhibits target-dependent tumor cell killing in vitro and in vivo.
Figures
References
-
- Garrett C. R., Eng C. (2011) Cetuximab in the treatment of patients with colorectal cancer. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 11, 937–949 - PubMed
-
- Alley S. C., Okeley N. M., Senter P. D. (2010) Antibody-drug conjugates. Targeted drug delivery for cancer. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 14, 529–537 - PubMed
-
- Schallreuter K. U., Kothari S., Chavan B., Spencer J. D. (2008) Regulation of melanogenesis. Controversies and new concepts. Exp. Dermatol. 17, 395–404 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

