Evidence that formation of vimentin mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) complex mediates mast cell activation following FcεRI/CC chemokine receptor 1 cross-talk
- PMID: 22613718
- PMCID: PMC3397876
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.319624
Evidence that formation of vimentin mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) complex mediates mast cell activation following FcεRI/CC chemokine receptor 1 cross-talk
Abstract
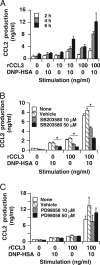
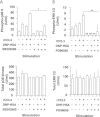
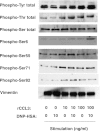
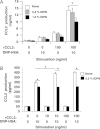
Accumulating evidence points to cross-talk between FcεRI and CC chemokine receptor (CCR)-mediated signaling pathways in mast cells. Here, we propose that vimentin, a protein comprising type III intermediate filament, participates in such cross-talk for CCL2/monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1) production in mast cells, which is a mechanism for allergic inflammation. Co-stimulation via FcεRI, using IgE/antigen, and CCR1, using recombinant CCL3/macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α), increased expression of phosphorylated, disassembled, and soluble vimentin in rat basophilic leukemia (RBL)-2H3 cells expressing human CCR1 (RBL-CCR1 cells) and bone marrow-derived murine mast cells, both models of mucosal type mast cells. Furthermore, co-stimulation enhanced production of CCL2 as well as phosphorylation of MAPK. Treating the cells with p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580, but not with MEK inhibitor PD98058, reduced CCL2 production, suggesting that p38 MAPK, but not ERK1/2, plays a critical role in the chemokine production. Immunoprecipitation analysis showed that vimentin interacts with phosphorylated ERK1/2 and p38 MAPKs in the co-simulated cells. Preventing disassembly of the vimentin by aggregating vimentin filaments using β,β'-iminodipropionitrile reduced the interaction of vimentin with phosphorylated MAPKs as well as CCL2 production in the cells. Taken together, disassembled vimentin interacting with phosphorylated p38 MAPK could mediate CCL2 production in mast cells upon FcεRI and CCR1 activation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
p38 MAPK and ERK activation by 9-cis-retinoic acid induces chemokine receptors CCR1 and CCR2 expression in human monocytic THP-1 cells.Exp Mol Med. 2007 Apr 30;39(2):129-38. doi: 10.1038/emm.2007.15. Exp Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17464174
-
Impact of engagement of FcepsilonRI and CC chemokine receptor 1 on mast cell activation and motility.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 12;279(46):48443-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408725200. Epub 2004 Aug 26. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15337751
-
Role of CC chemokines and their receptors in multiple aspects of mast cell biology: comparative protein profiling of FcepsilonRI- and/or CCR1-engaged mast cells using protein chip technology.Novartis Found Symp. 2005;271:131-40; discussion 140-51. Novartis Found Symp. 2005. PMID: 16605132
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling and ERK1/2 bistability in asthma.Clin Exp Allergy. 2011 Feb;41(2):149-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2010.03658.x. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011. PMID: 21121982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory Role of CCR1 in the Central Nervous System.Neuroimmunomodulation. 2024;31(1):173-182. doi: 10.1159/000540460. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2024. PMID: 39116843 Review.
Cited by
-
Vimentin modulates apoptosis and inflammatory cytokine release by a human monocytic cell line (THP-1) in response to lipopolysaccharides in vitro.Chin Med J (Engl). 2019 Jun 5;132(11):1336-1343. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000187. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019. PMID: 30882463 Free PMC article.
-
PKC activation in Niemann pick C1 cells restores subcellular cholesterol transport.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 15;8(8):e74169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074169. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23977398 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Angiogenic Factor Productions by Quercetin In Vitro and In Vivo.Medicines (Basel). 2021 May 12;8(5):22. doi: 10.3390/medicines8050022. Medicines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34065895 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of JTE013 abrogates experimental asthma by regulating proinflammatory cytokine production from bronchial epithelial cells.Respir Res. 2016 Nov 9;17(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12931-016-0465-x. Respir Res. 2016. PMID: 27829417 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of vimentin in the generation and secretion of extracellular vimentin in response to inflammation.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Apr 18;23(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02194-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40251523 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abramson J., Pecht I. (2007) Regulation of the mast cell response to the type 1 Fc ϵ receptor. Immunol. Rev. 217, 231–254 - PubMed
-
- Gilfillan A. M., Tkaczyk C. (2006) Integrated signaling pathways for mast cell activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6, 218–230 - PubMed
-
- Ono S. J., Nakamura T., Miyazaki D., Ohbayashi M., Dawson M., Toda M. (2003) Chemokines. Roles in leukocyte development, trafficking, and effector function. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 111, 1185–1199; quiz 1200 - PubMed
-
- Beer F., Kuo C. H., Morohoshi K., Goodliffe J., Munro P., Aye C. C., Dawson M., Richardson R. M., Jones L. H., Ikeda Y., Nakamura T., Toda M., Flynn T., Ohbayashi M., Miyazaki D., Ono S. J. (2007) Role of β-chemokines in mast cell activation and type I hypersensitivity reactions in the conjunctiva. In vivo and in vitro studies. Immunol. Rev. 217, 96–104 - PubMed
-
- Tominaga T., Miyazaki D., Sasaki S., Mihara S., Komatsu N., Yakura K., Inoue Y. (2009) Blocking mast cell-mediated type I hypersensitivity in experimental allergic conjunctivitis by monocyte chemoattractant protein-1/CCR2. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 50, 5181–5188 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

