Model for MLL translocations in therapy-related leukemia involving topoisomerase IIβ-mediated DNA strand breaks and gene proximity
- PMID: 22615413
- PMCID: PMC3384169
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1204406109
Model for MLL translocations in therapy-related leukemia involving topoisomerase IIβ-mediated DNA strand breaks and gene proximity
Abstract
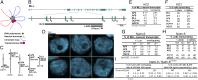
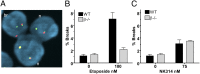
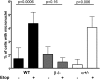
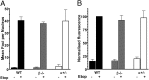
Topoisomerase poisons such as the epipodophyllotoxin etoposide are widely used effective cytotoxic anticancer agents. However, they are associated with the development of therapy-related acute myeloid leukemias (t-AMLs), which display characteristic balanced chromosome translocations, most often involving the mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) locus at 11q23. MLL translocation breakpoints in t-AMLs cluster in a DNase I hypersensitive region, which possesses cryptic promoter activity, implicating transcription as well as topoisomerase II activity in the translocation mechanism. We find that 2-3% of MLL alleles undergoing transcription do so in close proximity to one of its recurrent translocation partner genes, AF9 or AF4, consistent with their sharing transcription factories. We show that most etoposide-induced chromosome breaks in the MLL locus and the overall genotoxicity of etoposide are dependent on topoisomerase IIβ, but that topoisomerase IIα and -β occupancy and etoposide-induced DNA cleavage data suggest factors other than local topoisomerase II concentration determine specific clustering of MLL translocation breakpoints in t-AML. We propose a model where DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) introduced by topoisomerase IIβ into pairs of genes undergoing transcription within a common transcription factory become stabilized by antitopoisomerase II drugs such as etoposide, providing the opportunity for illegitimate end joining and translocation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Near-precise interchromosomal recombination and functional DNA topoisomerase II cleavage sites at MLL and AF-4 genomic breakpoints in treatment-related acute lymphoblastic leukemia with t(4;11) translocation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Aug 14;98(17):9802-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.171309898. Epub 2001 Aug 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11493704 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal DNA topoisomerase II cleavage events at 5'-TATTA-3' sequences in MLL and AF-9 create homologous single-stranded overhangs that anneal to form der(11) and der(9) genomic breakpoint junctions in treatment-related AML without further processing.Oncogene. 2003 Nov 20;22(52):8448-59. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207052. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 14627986
-
The broken MLL gene is frequently located outside the inherent chromosome territory in human lymphoid cells treated with DNA topoisomerase II poison etoposide.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 25;8(9):e75871. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075871. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24086652 Free PMC article.
-
Etoposide and illegitimate DNA double-strand break repair in the generation of MLL translocations: new insights and new questions.DNA Repair (Amst). 2006 Sep 8;5(9-10):1109-18. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.05.018. Epub 2006 Jun 30. DNA Repair (Amst). 2006. PMID: 16809075 Review.
-
Secondary leukemias induced by topoisomerase-targeted drugs.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Oct 1;1400(1-3):233-55. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(98)00139-0. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. PMID: 9748598 Review.
Cited by
-
The structure of DNA-bound human topoisomerase II alpha: conformational mechanisms for coordinating inter-subunit interactions with DNA cleavage.J Mol Biol. 2012 Dec 7;424(3-4):109-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.07.014. Epub 2012 Jul 25. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22841979 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Quinacrine as a Potent Topo II and Hsp90 Dual-Target Inhibitor, Repurposing for Cancer Therapy.Molecules. 2022 Aug 29;27(17):5561. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175561. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36080326 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-based design, synthesis and biological testing of etoposide analog epipodophyllotoxin-N-mustard hybrid compounds designed to covalently bind to topoisomerase II and DNA.Bioorg Med Chem. 2014 Nov 1;22(21):5935-49. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2014.09.014. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Bioorg Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25282653 Free PMC article.
-
Phenanthriplatin Acts As a Covalent Poison of Topoisomerase II Cleavage Complexes.ACS Chem Biol. 2016 Nov 18;11(11):2996-3001. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.6b00565. Epub 2016 Oct 6. ACS Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 27648475 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of DNA topoisomerase IIα splice variants on acquired drug resistance.Cancer Drug Resist. 2020;3(2):161-170. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2019.117. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Cancer Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 32566920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marshall WF, et al. Interphase chromosomes undergo constrained diffusional motion in living cells. Curr Biol. 1997;7:930–939. - PubMed
-
- Chubb JR, Boyle S, Perry P, Bickmore WA. Chromatin motion is constrained by association with nuclear compartments in human cells. Curr Biol. 2002;12:439–445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

