The effects of magnetite (Fe₃O₄) nanoparticles on electroporation-induced inward currents in pituitary tumor (GH₃) cells and in RAW 264.7 macrophages
- PMID: 22615532
- PMCID: PMC3357052
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S28798
The effects of magnetite (Fe₃O₄) nanoparticles on electroporation-induced inward currents in pituitary tumor (GH₃) cells and in RAW 264.7 macrophages
Abstract
Aims: Fe₃O₄ nanoparticles (NPs) have been known to provide a distinct image contrast effect for magnetic resonance imaging owing to their super paramagnetic properties on local magnetic fields. However, the possible effects of these NPs on membrane ion currents that concurrently induce local magnetic field perturbation remain unclear.
Methods: We evaluated whether amine surface-modified Fe₃O₄ NPs have any effect on ion currents in pituitary tumor (GH₃) cells via voltage clamp methods.
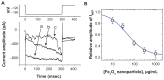
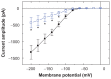
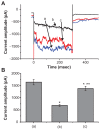
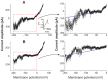
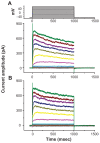
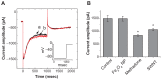
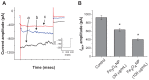
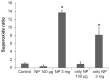
Results: The addition of Fe₃O₄ NPs decreases the amplitude of membrane electroporation-induced currents (I(MEP)) with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration at 45 μg/mL. Fe₃O₄ NPs at a concentration of 3 mg/mL produced a biphasic response in the amplitude of I(MEP), ie, an initial decrease followed by a sustained increase. A similar effect was also noted in RAW 264.7 macrophages.
Conclusion: The modulation of magnetic electroporation-induced currents by Fe₃O₄ NPs constitutes an important approach for cell tracking under various imaging modalities or facilitated drug delivery.
Keywords: free radical; ion current; iron oxide.
Figures
References
-
- Oghabian MA, Gharehaghaji N, Amirmohseni S, Khoei S, Guiti M. Detection sensitivity of lymph nodes of various sizes using USPIO nanoparticles in magnetic resonance imaging. Nanomedicine. 2010;6(3):496–499. - PubMed
-
- Shieh DB, Cheng FY, Su CH, et al. Aqueous dispersions of magnetite nanoparticles with NH3+ surfaces for magnetic manipulations of biomolecules and MRI contrast agents. Biomaterials. 2005;26(34):7183–7191. - PubMed
-
- Wu PC, Su CH, Cheng FY, et al. Modularly assembled magnetite nanoparticles enhance in vivo targeting for magnetic resonance cancer imaging. Bioconjug Chem. 2008;19(10):1972–1979. - PubMed
-
- Hughes S, El Haj AJ, Dobson J. Magnetic micro- and nanoparticle mediated activation of mechanosensitive ion channels. Med Eng Phys. 2005;27(9):754–762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

