An efficient procedure for purification of recombinant human β heat shock protein 90
- PMID: 22615596
- PMCID: PMC3232084
An efficient procedure for purification of recombinant human β heat shock protein 90
Abstract
Background and the purpose of the study: Heat Shock Protein 90 (Hsp90) is typically the most abundant chaperone in the eukaryotic cell cytoplasm, and its expression is essential for loading immunogenic peptides onto major histocompatibility complex molecules for presentation to T-cells. Therefore, it may act as a good candidate as an adjuvant molecule in vaccine technology.
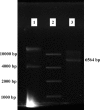
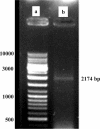
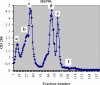
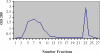
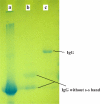
Methods: Initially the human Hsp90β gene was cloned into the heat inducible expression vector pGP1-2 and then the recombinant protein was isolated by ion exchange chromatography. After intradermal injection of confirmed purified band of protein to rabbits and isolation of the serum IgG antibody, for its affinity purification, the rabbit's purified Hsp90 specific IgG was coupled to the cyanogen bromide-activated Sepharose 4B.
Results: The recovery of the purified protein of interest by affinity chromatography was 50%.
Conclusion: This research enabled purification of human heat shock protein by a laboratory prepared column chromatography.
Keywords: CNBr activated Sepharose 4B; Head shock protein 90(Hsp90); Rabbit IgG; pGP1-2.
Figures




References
-
- Barginear MF, Van PC, Rosen N, Modi S, Hudis CA, Budman DR. The heat shock protein 90 chaperone complex: an evolving therapeutic target. Curr Cancer Drug Tar. 2008;8:522–532. - PubMed
-
- Smith DF, Whiteseli L, Katsanis E. Molecular Chaperones: Biology and Prospects for Pharmacological Intervention. Pharmacol Rev. 1998;4:493–514. - PubMed
-
- Minami M, Nakamura M, Emori Y, Minami Y. Both the N- and C- terminal chaperone sites of Hsp90 participate in protein refolding. Eur J Biochem. 2001;268:2520–2524. - PubMed
-
- Przepiorka D, Srivastava PK. Heat Shock protein-peptide complexes as immunotherapy for human cancer. Mol Med Today. 1998;4:478–484. - PubMed
-
- Basu S, Srivastava P. Fever-like temperature induces maturation of dendritic cells through induction of Hsp90. Int Immunol. 2003;15:1053–1061. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
