Redox, haem and CO in enzymatic catalysis and regulation
- PMID: 22616859
- PMCID: PMC3553215
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20120083
Redox, haem and CO in enzymatic catalysis and regulation
Abstract
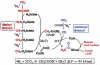
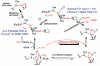
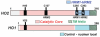
The present paper describes general principles of redox catalysis and redox regulation in two diverse systems. The first is microbial metabolism of CO by the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway, which involves the conversion of CO or H2/CO2 into acetyl-CoA, which then serves as a source of ATP and cell carbon. The focus is on two enzymes that make and utilize CO, CODH (carbon monoxide dehydrogenase) and ACS (acetyl-CoA synthase). In this pathway, CODH converts CO2 into CO and ACS generates acetyl-CoA in a reaction involving Ni·CO, methyl-Ni and acetyl-Ni as catalytic intermediates. A 70 Å (1 Å=0.1 nm) channel guides CO, generated at the active site of CODH, to a CO 'cage' near the ACS active site to sequester this reactive species and assure its rapid availability to participate in a kinetically coupled reaction with an unstable Ni(I) state that was recently trapped by photolytic, rapid kinetic and spectroscopic studies. The present paper also describes studies of two haem-regulated systems that involve a principle of metabolic regulation interlinking redox, haem and CO. Recent studies with HO2 (haem oxygenase-2), a K+ ion channel (the BK channel) and a nuclear receptor (Rev-Erb) demonstrate that this mode of regulation involves a thiol-disulfide redox switch that regulates haem binding and that gas signalling molecules (CO and NO) modulate the effect of haem.
Figures


References
-
- Pollack HN. A World Without Ice. Avery/Penguin Group; London: 2009.
-
- Fuchs G. Alternative pathways of carbon dioxide fixation: insights into the early evolution of life? Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2011;65:631–658. - PubMed
-
- Doukov TI, Iverson T, Seravalli J, Ragsdale SW, Drennan CL. A Ni–Fe–Cu center in a bifunctional carbon monoxide dehydrogenase/acetyl-CoA synthase. Science. 2002;298:567–572. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Y1-GM-1104/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM048242/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM039451/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM065440/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM069857/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 AG027349/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- GM39451/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM69857/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AG027349/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- GM48242/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM065318/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R29 GM048242/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102662/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- GM65440/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL 102662/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES017885/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM039451/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM065318/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

