Drugging Wnt signalling in cancer
- PMID: 22617421
- PMCID: PMC3380214
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.126
Drugging Wnt signalling in cancer
Erratum in
- EMBO J. 2012 Aug;31(15):3375
Abstract
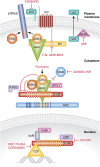
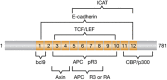
Aberrant regulation of the Wnt signalling pathway has emerged as a prevalent theme in cancer biology. This chapter summarizes the research that provides a proof of concept for inhibiting Wnt signalling in cancer, the potential means by which this could be achieved, and some recent advances towards this goal. A brief discussion of molecular diagnostics and possible safety concerns is also provided.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abrahamsson AE, Geron I, Gotlib J, Dao KH, Barroga CF, Newton IG, Giles FJ, Durocher J, Creusot RS, Karimi M, Jones C, Zehnder JL, Keating A, Negrin RS, Weissman IL, Jamieson CH (2009) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta missplicing contributes to leukemia stem cell generation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 3925–3929 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashihara E, Kawata E, Nakagawa Y, Shimazaski C, Kuroda J, Taniguchi K, Uchiyama H, Tanaka R, Yokota A, Takeuchi M, Kamitsuji Y, Inaba T, Taniwaki M, Kimura S, Maekawa T (2009) Beta-catenin small interfering RNA successfully suppressed progression of multiple myeloma in a mouse model. Clin Cancer Res 15: 2731–2738 - PubMed
-
- Bafico A, Liu G, Goldin L, Harris V, Aaronson SA (2004) An autocrine mechanism for constitutive Wnt pathway activation in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell 6: 497–506 - PubMed
-
- Behrens J, von Kries JP, Kuhl M, Bruhn L, Wedlich D, Grosschedl R, Birchmeier W (1996) Functional interaction of beta-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature 382: 638–642 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

