The many faces and functions of β-catenin
- PMID: 22617422
- PMCID: PMC3380220
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.150
The many faces and functions of β-catenin
Abstract
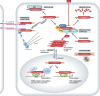
β-Catenin (Armadillo in Drosophila) is a multitasking and evolutionary conserved molecule that in metazoans exerts a crucial role in a multitude of developmental and homeostatic processes. More specifically, β-catenin is an integral structural component of cadherin-based adherens junctions, and the key nuclear effector of canonical Wnt signalling in the nucleus. Imbalance in the structural and signalling properties of β-catenin often results in disease and deregulated growth connected to cancer and metastasis. Intense research into the life of β-catenin has revealed a complex picture. Here, we try to capture the state of the art: we try to summarize and make some sense of the processes that regulate β-catenin, as well as the plethora of β-catenin binding partners. One focus will be the interaction of β-catenin with different transcription factors and the potential implications of these interactions for direct cross-talk between β-catenin and non-Wnt signalling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Adamska M, Larroux C, Adamski M, Green K, Lovas E, Koop D, Richards GS, Zwafink C, Degnan BM (2010) Structure and expression of conserved Wnt pathway components in the demosponge Amphimedon queenslandica. Evol Dev 12: 494–518 - PubMed
-
- Angers S, Moon RT (2009) Proximal events in Wnt signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10: 468–477 - PubMed
-
- Ansieau S, Morel AP, Hinkal G, Bastid J, Puisieux A (2010) TWISTing an embryonic transcription factor into an oncoprotein. Oncogene 29: 3173–3184 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

