Histochemical and biochemical analysis of the size-dependent nanoimmunoresponse in mouse Peyer's patches using fluorescent organosilica particles
- PMID: 22619503
- PMCID: PMC3356209
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S28675
Histochemical and biochemical analysis of the size-dependent nanoimmunoresponse in mouse Peyer's patches using fluorescent organosilica particles
Abstract
Background/objective: The size-dependent mucosal immunoresponse against nanomaterials (nanoimmunoresponse) is an important approach for mucosal vaccination. In the present work, the size-dependent nanoimmunoresponse of mouse Peyer's patches (PPs) and immunoglobulin A (IgA) level was investigated using fluorescent thiol-organosilica particles.
Methods: Various sizes of fluorescent thiol-organosilica particles (100, 180, 365, 745, and 925 nm in diameter) were administered orally. PPs were analyzed histochemically, and IgA levels in PP homogenates, intestinal secretions around PPs, and bile were analyzed biochemically.
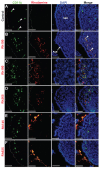
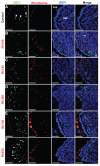
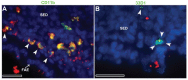
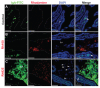
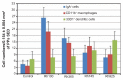
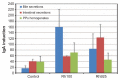
Results: When compared with the larger particles (745 and 925 nm), oral administration of smaller thiol-organosilica particles (100, 180, and 365 nm) increased the number of CD11b(+) macrophages and IgA(+) cells in the subepithelial domes of the PPs. Additionally, administration of larger particles induced the expression of alpha-L-fucose and mucosal IgA on the surface of M cells in the follicle-associated epithelia of PPs and increased the number of 33D1(+) dendritic cells in the subepithelial domes of the PPs. IgA contents in the bile and PP homogenates were high after the administration of the 100 nm particles, but IgA levels in the intestinal secretions were high after the administration of the 925 nm particles. Two size-dependent routes of IgA secretions into the intestinal lumen, the enterohepatic route for smaller particles and the mucosal route for larger particles were proposed.
Conclusion: Thiol-organosilica particles demonstrated size-dependent nanoimmunoresponse after oral administration. The size of the particles may control the mucosal immunity in PPs and were useful in mucosal vaccination approaches.
Keywords: IgA; Peyer’s patches immune cells; mucosal vaccination; thiol-organosilica particles.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Imaging of size-dependent uptake and identification of novel pathways in mouse Peyer's patches using fluorescent organosilica particles.Nanomedicine. 2012 Jul;8(5):627-36. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2011.08.009. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 21889475
-
Alternate mucosal immune system: organized Peyer's patches are not required for IgA responses in the gastrointestinal tract.J Immunol. 2000 May 15;164(10):5184-91. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.10.5184. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10799877
-
Distinct roles for Peyer's patch B cells for induction of antigen-specific IgA antibody responses in mice administered oral recombinant Salmonella.Int Immunol. 2019 Jul 30;31(8):531-541. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxz029. Int Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30868152
-
Intestinal Peyer's Patches: Structure, Function, and In Vitro Modeling.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023 Jun;20(3):341-353. doi: 10.1007/s13770-023-00543-y. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023. PMID: 37079198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Keynote review: intestinal Peyer's patch M cells and oral vaccine targeting.Drug Discov Today. 2005 Sep 1;10(17):1145-57. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6446(05)03536-1. Drug Discov Today. 2005. PMID: 16182207 Review.
Cited by
-
Size-dependent biodistribution of thiol-organosilica nanoparticles and F4/80 protein expression in the genital tract of female mice after intravaginal administration.Histochem Cell Biol. 2021 Jun;155(6):683-698. doi: 10.1007/s00418-021-01974-1. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Histochem Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33656583
-
A simple method for the quantification of molecular decorations on silica particles.Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2014 Jan 3;15(1):015002. doi: 10.1088/1468-6996/15/1/015002. eCollection 2014 Feb. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2014. PMID: 27877644 Free PMC article.
-
Mesoscopic Multimodal Imaging Provides New Insight to Tumor Tissue Evaluation: An Example of Macrophage Imaging of Hepatic Tumor using Organosilica Nanoparticles.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 21;7(1):3953. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04043-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28638087 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of Nanoparticles Including Antisolvent Drugs by the Combination of Roll Milling and High-pressure Homogenization.Curr Nanosci. 2018 Apr;14(2):143-147. doi: 10.2174/1573413713666171109155955. Curr Nanosci. 2018. PMID: 30079002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Salman HH, Irache JM, Gamazo C. Immunoadjuvant capacity of flagellin and mannosamine-coated poly(anhydride) nanoparticles in oral vaccination. Vaccine. 2009;27(35):4784–4790. - PubMed
-
- Salman HH, Gamazo C, Agüeros M, Irache JM. Bioadhesive capacity and immunoadjuvant properties of thiamine-coated nanoparticles. Vaccine. 2007;25(48):8123–8132. - PubMed
-
- Chabot S, Wagner JS, Farrant S, Neutra MR. TLRs regulate the gatekeeping functions of the intestinal follicle-associated epithelium. J Immun. 2006;176(7):4275–4283. - PubMed
-
- Semete B, Booysen LI, Kalombo L, et al. In vivo uptake and acute immune response to orally administered chitosan and PEG coated PLGA nanoparticles. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010;249(2):158–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

