Clinical characteristics of spinal levobupivacaine: hyperbaric compared with isobaric solution
- PMID: 22619612
- PMCID: PMC3349113
- DOI: 10.1100/2012/169076
Clinical characteristics of spinal levobupivacaine: hyperbaric compared with isobaric solution
Abstract
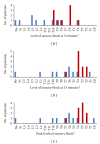
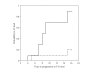
We performed a prospective, double-blinded study in 20 patients undergoing gynecologic surgery with lower abdominal incision, to investigate characteristics of intrathecal hyperbaric levobupivacaine compared with isobaric levobupivacaine. We randomly assigned them to receive 3 mL of either isobaric or hyperbaric 0.42% levobupivacaine intrathecally. We found that hyperbaric levobupivacaine, compared with isobaric levobupivacaine, spread faster to T10 level (2.8 ± 1.1 versus 6.6 ± 4.7 minutes, P = 0.039), reached higher sensory block levels at 5 and 15 minutes after injection (T8 versus L1, P = 0.011, and T4 versus T7, P = 0.027, resp.), and had a higher peak level (T4 versus T8, P = 0.040). Isobaric levobupivacaine caused a wider range of peak levels (L1 to C8) compared with hyperbaric form (T7 to T2). The level of T4 or higher reached 90% in the hyperbaric group compared with 20% in the isobaric group (P = 0.005). Our results suggest that hyperbaric levobupivacaine was more predictable for sensory block level and more effective for surgical procedures with lower abdominal approach. Hyperbaric levobupivacaine seems to be suitable, but the optimal dosage needs further investigation.
Figures
References
-
- Camorcia M, Capogna G, Berritta C, Columb MO. The relative potencies for motor block after intrathecal ropivacaine, levobupivacaine, and bupivacaine. Anesthesia and Analgesia. 2007;104(4):904–907. - PubMed
-
- Cappelleri G, Aldegheri G, Danelli G, et al. Spinal anesthesia with hyperbaric levobupivacaine and ropivacaine for outpatient knee arthroscopy: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study. Anesthesia and Analgesia. 2005;101(1):77–82. - PubMed
-
- Casati A, Moizo E, Marchetti C, Vinciguerra F. A prospective, randomized, double-blind comparison of unilateral spinal anesthesia with hyperbaric bupivacaine, ropivacaine, or levobupivacaine for inguinal herniorrhaphy. Anesthesia and Analgesia. 2004;99(5):1387–1392. - PubMed
-
- Vanna O, Chumsang L, Thongmee S. Levobupivacaine and bupivacaine in spinal anesthesia for transurethral endoscopic surgery. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand. 2006;89(8):1133–1139. - PubMed
-
- Sen H, Purtuloglu T, Sizlan A, et al. Comparison of intrathecal hyperbaric and isobaric levobupivacaine in urological surgery. Minerva Anestesiologica. 2010;76(1):24–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

