Integrated Use of Biomarkers (O : N Ratio and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition) on Aulacomya ater (Molina, 1782) (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) as a Criteria for Effects of Organophosphate Pesticide Exposition
- PMID: 22619673
- PMCID: PMC3348645
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/951568
Integrated Use of Biomarkers (O : N Ratio and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition) on Aulacomya ater (Molina, 1782) (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) as a Criteria for Effects of Organophosphate Pesticide Exposition
Abstract
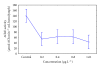
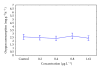
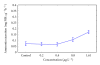
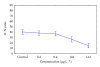
The effect of residual concentrations of organophosphate pesticide chlorpyrifos (Lorsban 4E) on the activity of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme and oxygen : nitrogen ratio in the mussel Aulacomya ater was analyzed. Toxicity tests show a sensitivity to the pesticide in the bivalve estimated at 16 μg L(-1) (LC(50-96 hours)). Concentrations between 0.2 and 1.61 μg L(-1) were able to inhibit significantly the AChE activity, and concentrations between 0.8 and 1.61 μg L(-1) stimulate ammonia excretion and decrease oxygen : ammonia-N (O : N) ratio, with respect to the control group. A. ater proved to be a species sensitive to pesticide exposure and easy to handle in lab conditions. Thus, it is recommended as a bioindicator for use in programs of environmental alertness in the Eastern South Pacific coastal zone.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of hemocyte properties from Mytilus edulis desolationis and Aulacomya ater in the Kerguelen Islands.Mar Environ Res. 2015 Sep;110:174-82. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2015.09.003. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Mar Environ Res. 2015. PMID: 26382607
-
Further considerations of the skeletal system as a biomarker of episodic chlorpyrifos exposure.Aquat Toxicol. 2001 May;52(3-4):285-96. doi: 10.1016/s0166-445x(00)00164-8. Aquat Toxicol. 2001. PMID: 11239688
-
The sensitivity of grass shrimp, Palaemonetes pugio, embryos to organophosphate pesticide induced acetylcholinesterase inhibition.Aquat Toxicol. 2000 Mar 1;48(2-3):127-134. doi: 10.1016/s0166-445x(99)00053-3. Aquat Toxicol. 2000. PMID: 10686320
-
Characterization of the mechanical properties of tough biopolymer fibres from the mussel byssus of Aulacomya ater.Acta Biomater. 2008 Jul;4(4):1114-7. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2008.01.014. Epub 2008 Feb 7. Acta Biomater. 2008. PMID: 18321800
-
Refined avian risk assessment for chlorpyrifos in the United States.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2014;231:163-217. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-03865-0_6. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24723136 Review.
Cited by
-
Genotoxic, cytotoxic, and neurotoxic responses in Anodonta cygnea after complex metal mixture treatment.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Mar;26(8):7627-7639. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04206-1. Epub 2019 Jan 21. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30666580
References
-
- Apeti DA, Lauenstein GG, Christensen JD, et al. A historical assessment of coastal contamination in Birch Harbor, Maine based on the analysis of mussels collected in the 1940s and the Mussel Watch Program. Marine Pollution Bulletin. 2010;60(5):732–742. - PubMed
-
- Canty MN, Hagger JA, Moore RTB, Cooper L, Galloway TS. Sublethal impact of short term exposure to the organophosphate pesticide azamethiphos in the marine mollusc Mytilus edulis . Marine Pollution Bulletin. 2007;54(4):396–402. - PubMed
-
- Bayne B, Moore MN, Widdows J, Livingstone DR, Salkeld P. Measurement of the responses of individuals to environmental stress and pollution: studies with bivalve mollusks. Philosophycal Transcript of Royal Society of London B. 1979;286(1015):563–581. - PubMed
-
- Richardson BJ, Mak E, De Luca-Abbott SB, Martin M, McClellan K, Lam PKS. Antioxidant responses to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine pesticides in green-lipped mussels (Perna viridis): do mussels “integrate” biomarker responses? Marine Pollution Bulletin. 2008;57(6–12):503–514. - PubMed
-
- Rickwood CJ, Galloway TS. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition as a biomarker of adverse effect: a study of Mytilus edulis exposed to the priority pollutant chlorfenvinphos. Aquatic Toxicology. 2004;67(1):45–56. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

