Randomized controlled trial of the effectiveness of genetic counseling and a distance, computer-based, lifestyle intervention program for adult offspring of patients with type 2 diabetes: background, study protocol, and baseline patient characteristics
- PMID: 22619705
- PMCID: PMC3350978
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/831735
Randomized controlled trial of the effectiveness of genetic counseling and a distance, computer-based, lifestyle intervention program for adult offspring of patients with type 2 diabetes: background, study protocol, and baseline patient characteristics
Abstract
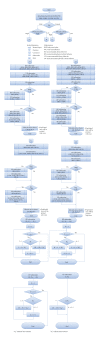
Relatives of type 2 diabetic patients are at a high risk of developing type 2 diabetes and should be regarded as target of intervention for diabetes prevention. However, it is usually hard to motivate them to implement preventive lifestyle changes, because of lack of opportunity to take advises from medical professionals, inadequate risk perception, and low priority for preventive behavior. Prevention strategy for them therefore should be highly acceptable and suited for them. The parallel, three-group trial is now being conducted to investigate the effects of genetic counseling and/or a computerized behavioral program on the prevention of type 2 diabetes in that population. The preventive strategies used in this study could provide a novel solution to the numbers of genetically high-risk individuals, if found to be effective. The objective of this paper is to describe the background, protocol, and baseline patient characteristics of the trial.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of genetic counseling for adult offspring of patients with type 2 diabetes on attitudes toward diabetes and its heredity: a randomized controlled trial.J Genet Couns. 2014 Oct;23(5):762-9. doi: 10.1007/s10897-013-9680-5. Epub 2014 Jan 8. J Genet Couns. 2014. PMID: 24399094 Clinical Trial.
-
Cost-effectiveness of a lifestyle intervention in high-risk individuals for diabetes in a low- and middle-income setting: Trial-based analysis of the Kerala Diabetes Prevention Program.BMC Med. 2020 Sep 4;18(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s12916-020-01704-9. BMC Med. 2020. PMID: 32883279 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A peer-support lifestyle intervention for preventing type 2 diabetes in India: A cluster-randomized controlled trial of the Kerala Diabetes Prevention Program.PLoS Med. 2018 Jun 6;15(6):e1002575. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002575. eCollection 2018 Jun. PLoS Med. 2018. PMID: 29874236 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Computer-supported indirect-form lifestyle-modification support program using Lifestyle Intervention Support Software for Diabetes Prevention (LISS-DP) for people with a family history of type 2 diabetes in a medical checkup setting: a randomized controlled trial.Prim Care Diabetes. 2014 Oct;8(3):207-14. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2014.01.007. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Prim Care Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24529485 Clinical Trial.
-
Nurse-led motivational interviewing to change the lifestyle of patients with type 2 diabetes (MILD-project): protocol for a cluster, randomized, controlled trial on implementing lifestyle recommendations.BMC Health Serv Res. 2009 Jan 30;9:19. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-9-19. BMC Health Serv Res. 2009. PMID: 19183462 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Research gaps and opportunities in precision nutrition: an NIH workshop report.Am J Clin Nutr. 2022 Dec 19;116(6):1877-1900. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqac237. Am J Clin Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36055772 Free PMC article.
-
Lifestyle behaviors that reduce food and fat intake in patients with type 2 diabetes within 3 months of diagnosis lead to a reduction in the HbA1c level after 12 months.Diabetol Int. 2023 Aug 10;14(4):413-421. doi: 10.1007/s13340-023-00650-0. eCollection 2023 Oct. Diabetol Int. 2023. PMID: 37781461 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary Efficacy, Feasibility, and Perceived Usefulness of a Smartphone-Based Self-Management System With Personalized Goal Setting and Feedback to Increase Step Count Among Workers With High Blood Pressure: Before-and-After Study.JMIR Cardio. 2023 Jul 21;7:e43940. doi: 10.2196/43940. JMIR Cardio. 2023. PMID: 37477976 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of genetic counseling for adult offspring of patients with type 2 diabetes on attitudes toward diabetes and its heredity: a randomized controlled trial.J Genet Couns. 2014 Oct;23(5):762-9. doi: 10.1007/s10897-013-9680-5. Epub 2014 Jan 8. J Genet Couns. 2014. PMID: 24399094 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Tuomilehto J, Lindström J, Eriksson JG, et al. Prevention of type 2 Diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2001;344(18):1343–1350. - PubMed
-
- Li G, Zhang P, Wang J, et al. The long-term effect of lifestyle interventions to prevent diabetes in the China Da Qing Diabetes Prevention Study: a 20-year follow-up study. The Lancet. 2008;371(9626):1783–1789. - PubMed
-
- Pan XR, Li GW, Hu YH, et al. Effects of diet and exercise in preventing NIDDM in people with impaired glucose tolerance: the Da Qing IGT and Diabetes study. Diabetes Care. 1997;20(4):537–544. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources