ZnT4 provides zinc to zinc-dependent proteins in the trans-Golgi network critical for cell function and Zn export in mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 22621784
- PMCID: PMC3423030
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00443.2011
ZnT4 provides zinc to zinc-dependent proteins in the trans-Golgi network critical for cell function and Zn export in mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
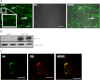
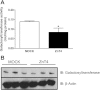
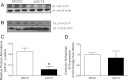
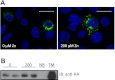
Zinc (Zn) transporter 4 (ZnT4) plays a key role in mammary gland Zn metabolism. A mutation in ZnT4 (SLC30A4) that targets the protein for degradation is responsible for the "lethal milk" (lm/lm) mouse phenotype. ZnT4 protein is only detected in the secreting mammary gland, and lm/lm mice have ∼35% less Zn in milk, decreased mammary gland size, and decreased milk secretion. However, the precise contribution of ZnT4 is unknown. We used cultured mouse mammary epithelial cells (HC11) and determined that ZnT4 was localized to the trans-Golgi network (TGN) and cell membrane and transported Zn from the cytoplasm. ZnT4-mediated Zn import into the TGN directly contributed to labile Zn accumulation as ZnT4 overexpression increased FluoZin3 fluorescence. Moreover, ZnT4 provided Zn for metallation of galactosyltransferase, a Zn-dependent protein localized within the TGN that is critical for milk secretion, and carbonic anhydrase VI, a Zn-dependent protein secreted from the TGN into milk. We further noted that ZnT4 relocalized to the cell membrane in response to Zn. Together these studies demonstrated that ZnT4 transports Zn into the TGN, which is critical for key secretory functions of the mammary cell.
Figures

References
-
- Apgar J. Effect of zinc deficiency on parturition in the rat. Am J Physiol 215: 160–163, 1968 - PubMed
-
- Ballan-Dufrancais C. Localization of metals in cells of pterygote insects. Microsc Res Tech 56: 403–420, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Bhatnagar S, Taneja S. Zinc and cognitive development. Br J Nutr 85, Suppl 2: S139–S145, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Bouchilloux S, Ferrand M, Gregoire J, Chabaud O. Localization in smooth microsomes from sheep thyroid of both a galactosyltransferase and an N-acetylhexosaminyltransferase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 37: 538–544, 1969 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

