ΔFosB in the supraoptic nucleus contributes to hyponatremia in rats with cirrhosis
- PMID: 22621966
- PMCID: PMC3404636
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00142.2012
ΔFosB in the supraoptic nucleus contributes to hyponatremia in rats with cirrhosis
Abstract
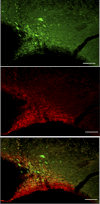
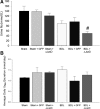
Bile duct ligation (BDL), a model of hepatic cirrhosis, is associated with dilutional hyponatremia and inappropriate vasopressin release. ΔFosB staining was significantly increased in vasopressin and oxytocin magnocellular neurosecretory cells in the supraoptic nucleus (SON) of BDL rats. We tested the role of SON ΔFosB in fluid retention following BDL by injecting the SON (n = 10) with 400 nl of an adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector expressing ΔJunD (a dominant negative construct for ΔFosB) plus green fluorescent protein (GFP) (AAV-GFP-ΔJunD). Controls were either noninjected or injected with an AAV vector expressing only GFP. Three weeks after BDL or sham ligation surgery, rats were individually housed in metabolism cages for 1 wk. Average daily water intake was significantly elevated in all BDL rats compared with sham ligated controls. Average daily urine output was significantly greater in AAV-GFP-ΔJunD-treated BDL rats compared with all other groups. Daily average urine sodium concentration was significantly lower in AAV-GFP-ΔJunD-treated BDL rats than the other groups, although average daily sodium excretion was not different among the groups. SON expression of ΔJunD produced a diuresis in BDL rats that may be related to decreased circulating levels of vasopressin or oxytocin. These findings support the view that ΔFosB expression in SON magnocellular secretory cells contribute to dilutional hyponatremia in BDL rats.
Figures



Similar articles
-
ANG II receptor subtype 1a gene knockdown in the subfornical organ prevents increased drinking behavior in bile duct-ligated rats.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014 Sep 15;307(6):R597-607. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00163.2014. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25009217 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of bile duct ligation on the inhibitory control of supraoptic vasopressin neurons.J Neuroendocrinol. 2023 Jun;35(6):e13312. doi: 10.1111/jne.13312. Epub 2023 Jun 19. J Neuroendocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37337093 Free PMC article.
-
Region-specific changes in transient receptor potential vanilloid channel expression in the vasopressin magnocellular system in hepatic cirrhosis-induced hyponatraemia.J Neuroendocrinol. 2012 Apr;24(4):642-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2011.02273.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22188460 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular regulation of supraoptic neurons in the rat: synaptic inputs and cellular signals.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2004 Feb-Apr;84(2-3):183-96. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2003.11.004. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 14769435 Review.
-
Hypervolemic Hyponatremia (Liver).Front Horm Res. 2019;52:104-112. doi: 10.1159/000493241. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Front Horm Res. 2019. PMID: 32097916 Review.
Cited by
-
AT1a influences GABAA-mediated inhibition through regulation of KCC2 expression.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018 Nov 1;315(5):R972-R982. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00105.2018. Epub 2018 Aug 29. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30156863 Free PMC article.
-
ANG II receptor subtype 1a gene knockdown in the subfornical organ prevents increased drinking behavior in bile duct-ligated rats.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014 Sep 15;307(6):R597-607. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00163.2014. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25009217 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II type 1a receptors in subfornical organ contribute towards chronic intermittent hypoxia-associated sustained increase in mean arterial pressure.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Mar 1;308(5):H435-46. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00747.2014. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25539713 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of bile duct ligation on the inhibitory control of supraoptic vasopressin neurons.J Neuroendocrinol. 2023 Jun;35(6):e13312. doi: 10.1111/jne.13312. Epub 2023 Jun 19. J Neuroendocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37337093 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Supraoptic Vasopressin Neurons in Hyponatremia.Neuroendocrinology. 2020;110(7-8):630-641. doi: 10.1159/000503723. Epub 2019 Sep 27. Neuroendocrinology. 2020. PMID: 31557760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstrong WE. Morphological and electrophysiological classification of hypothalamic supraoptic neurons. Prog Neurobiol 47: 291– 339, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Armstrong WE, Stern JE. Electrophysiological and morphological characteristics of neurons in perinuclear zone of supraoptic nucleus. J Neurophysiol 78: 2427– 2437, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Boudaba C, Schrader LA, Tasker JG. Physiological evidence for local excitatory synaptic circuits in the rat hypothalamus. J Neurophysiol 77: 3396– 3400, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Bourque CW, Oliet SH. Osmoreceptors in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Physiol 59: 601– 619, 1997 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

