MicroRNA-181b regulates NF-κB-mediated vascular inflammation
- PMID: 22622040
- PMCID: PMC3366408
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI61495
MicroRNA-181b regulates NF-κB-mediated vascular inflammation
Abstract
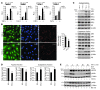
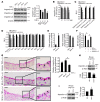
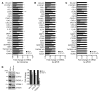
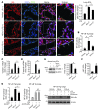
EC activation and dysfunction have been linked to a variety of vascular inflammatory disease states. The function of microRNAs (miRNAs) in vascular EC activation and inflammation remains poorly understood. Herein, we report that microRNA-181b (miR-181b) serves as a potent regulator of downstream NF-κB signaling in the vascular endothelium by targeting importin-α3, a protein that is required for nuclear translocation of NF-κB. Overexpression of miR-181b inhibited importin-α3 expression and an enriched set of NF-κB-responsive genes such as adhesion molecules VCAM-1 and E-selectin in ECs in vitro and in vivo. In addition, treatment of mice with proinflammatory stimuli reduced miR-181b expression. Rescue of miR-181b levels by systemic administration of miR-181b "mimics" reduced downstream NF-κB signaling and leukocyte influx in the vascular endothelium and decreased lung injury and mortality in endotoxemic mice. In contrast, miR-181b inhibition exacerbated endotoxin-induced NF-κB activity, leukocyte influx, and lung injury. Finally, we observed that critically ill patients with sepsis had reduced levels of miR-181b compared with control intensive care unit (ICU) subjects. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that miR-181b regulates NF-κB-mediated EC activation and vascular inflammation in response to proinflammatory stimuli and that rescue of miR-181b expression could provide a new target for antiinflammatory therapy and critical illness.
Figures




Comment in
-
Taming endothelial activation with a microRNA.J Clin Invest. 2012 Jun;122(6):1967-70. doi: 10.1172/JCI63818. Epub 2012 May 24. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22622035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guerci B, Bohme P, Kearney-Schwartz A, Zannad F, Drouin P. Endothelial dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Part 2: altered endothelial function and the effects of treatments in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. 2001;27(4 pt 1):436–447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

