Glycolytic oligodendrocytes maintain myelin and long-term axonal integrity
- PMID: 22622581
- PMCID: PMC3613737
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11007
Glycolytic oligodendrocytes maintain myelin and long-term axonal integrity
Abstract
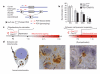
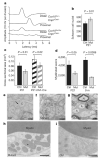
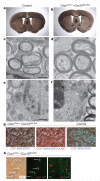
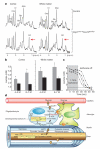
Oligodendrocytes, the myelin-forming glial cells of the central nervous system, maintain long-term axonal integrity. However, the underlying support mechanisms are not understood. Here we identify a metabolic component of axon-glia interactions by generating conditional Cox10 (protoheme IX farnesyltransferase) mutant mice, in which oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells fail to assemble stable mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase (COX, also known as mitochondrial complex IV). In the peripheral nervous system, Cox10 conditional mutants exhibit severe neuropathy with dysmyelination, abnormal Remak bundles, muscle atrophy and paralysis. Notably, perturbing mitochondrial respiration did not cause glial cell death. In the adult central nervous system, we found no signs of demyelination, axonal degeneration or secondary inflammation. Unlike cultured oligodendrocytes, which are sensitive to COX inhibitors, post-myelination oligodendrocytes survive well in the absence of COX activity. More importantly, by in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy, brain lactate concentrations in mutants were increased compared with controls, but were detectable only in mice exposed to volatile anaesthetics. This indicates that aerobic glycolysis products derived from oligodendrocytes are rapidly metabolized within white matter tracts. Because myelinated axons can use lactate when energy-deprived, our findings suggest a model in which axon-glia metabolic coupling serves a physiological function.
Figures
References
-
- Griffiths I, et al. Axonal swellings and degeneration in mice lacking the major proteolipid of myelin. Science. 1998;280:1610–1613. - PubMed
-
- Lappe-Siefke C, et al. Disruption of Cnp1 uncouples oligodendroglial functions in axonal support and myelination. Nature Genet. 2003;33:366–374. - PubMed
-
- Kassmann CM, et al. Axonal loss and neuroinflammation caused by peroxisome-deficient oligodendrocytes. Nature Genet. 2007;39:969–976. - PubMed
-
- Nave KA. Myelination and the trophic support of long axons. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 2010;11:275–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

