Paranasal sinus mucocele
- PMID: 22623085
- PMCID: PMC3422585
- DOI: 10.1007/s12105-012-0359-2
Paranasal sinus mucocele
Abstract
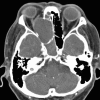
Paranasal sinus mucoceles are epithelium-lined cystic masses usually resulting from obstruction of sinus ostia. They most frequently occur in the frontal and ethmoid sinuses. While ophthalmologic symptoms are most common, patients also report rhinological or neurological complaints. The close proximity of paranasal sinus mucoceles to the orbit and skull base predisposes the patient to significant morbidity. Computed tomography displays a non-enhancing homogenous mass with expansion of bony walls. Magnetic resonance imaging reveals variable intensity of T1-weighted images and a hyperintense mass on T2-weighted images. Histopathologically mucoceles have features of respiratory mucosa with areas of reactive bone formation, hemorrhage, fibrosis, and granulation tissue. Surgical excision is the standard treatment with trends towards endoscopic techniques.
Figures



References
-
- Thompson LDR, Wenig BM. Mucocele of paranasal sinus. In: Diagnostic pathology: head and neck. Salt Lake City: Amirsys, 2011, p 45.
-
- Kao HW, Lo CP, Hsu YC, Chiu YC, Hsiao CH, Chen CY. Sphenoid sinus mucocele presenting with optic canal syndrome. J Med Sci. 2006;26(2):061–064.
-
- Lee TJ, Li SP, Fu CH, Huang CC, Chang PH, Chen YW, Chen CW. Extensive paranasal sinus mucoceles: a 15-year review of 82 cases. Am J Otolaryngol Head Neck Med Surg. 2009;30:234–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

