Relationship between chest compression rates and outcomes from cardiac arrest
- PMID: 22623717
- PMCID: PMC3388797
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.059535
Relationship between chest compression rates and outcomes from cardiac arrest
Abstract
Background: Guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation recommend a chest compression rate of at least 100 compressions per minute. Animal and human studies have reported that blood flow is greatest with chest compression rates near 120/min, but few have reported rates used during out-of-hospital (OOH) cardiopulmonary resuscitation or the relationship between rate and outcome. The purpose of this study was to describe chest compression rates used by emergency medical services providers to resuscitate patients with OOH cardiac arrest and to determine the relationship between chest compression rate and outcome.
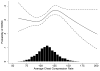
Methods and results: Included were patients aged ≥ 20 years with OOH cardiac arrest treated by emergency medical services providers participating in the Resuscitation Outcomes Consortium. Data were abstracted from monitor-defibrillator recordings during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Multiple logistic regression analysis assessed the association between chest compression rate and outcome. From December 2005 to May 2007, 3098 patients with OOH cardiac arrest were included in this study. Mean age was 67 ± 16 years, and 8.6% survived to hospital discharge. Mean compression rate was 112 ± 19/min. A curvilinear association between chest compression rate and return of spontaneous circulation was found in cubic spline models after multivariable adjustment (P=0.012). Return of spontaneous circulation rates peaked at a compression rate of ≈ 125/min and then declined. Chest compression rate was not significantly associated with survival to hospital discharge in multivariable categorical or cubic spline models.
Conclusions: Chest compression rate was associated with return of spontaneous circulation but not with survival to hospital discharge in OOH cardiac arrest.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Comment in
-
Chest compression rate: where is the sweet spot?Circulation. 2012 Jun 19;125(24):2968-70. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.112722. Epub 2012 May 23. Circulation. 2012. PMID: 22623716 No abstract available.
References
-
- Berg RA, Hemphill R, Abella BS, Aufderheide TP, Cave DM, Hazinski MF, Lerner EB, Rea TD, Sayre MR, Swor RA. Part 5: Adult basic life support. 2010 American Heart Association guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation. 2010;122:S685–S705. - PubMed
-
- Kouwenhoven WB, Jude JR, Knickerbocker GG. Closed-chest cardiac massage. JAMA. 1960;173:1064–1067. - PubMed
-
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation: Statement by the Ad Hoc Committee on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation of the Division of Medical Sciences, National Academy of Sciences – National Research Council. JAMA. 1966;198:138–145. - PubMed
-
- Standards and guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and emergency cardiac care (ECC) JAMA. 1986;255:2905–2984. - PubMed
-
- Koster RW, Baubin MA, Bossaert LL, Caballero A, Cassa P, Castrén M, Granja C, Handley AJ, Monsieurs KG, Perkins GD, Raffay V, Sandroni C. European Resuscitation Council guidelines for resuscitation 2010. Section 2: Adult basic life support and use of automated external defibrillators. Resuscitation. 2010;81:1277–1292. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 HL077866/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077871/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077867/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077887/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077881/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077873/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077871/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077881/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077908/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077887/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1 DCC 5U01 HL077863/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077885/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- U01 HL077865/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077863/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077908/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077872/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077866/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077873/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077867/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077885/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077865/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077872/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

