Neurogliaform and Ivy Cells: A Major Family of nNOS Expressing GABAergic Neurons
- PMID: 22623913
- PMCID: PMC3353154
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2012.00023
Neurogliaform and Ivy Cells: A Major Family of nNOS Expressing GABAergic Neurons
Abstract
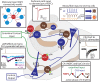
Neurogliaform and Ivy cells are members of an abundant family of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) expressing GABAergic interneurons found in diverse brain regions. These cells have a defining dense local axonal plexus, and display unique synaptic properties including a biphasic postsynaptic response with both a slow GABA(A) component and a GABA(B) component following even a single action potential. The type of transmission displayed by these cells has been termed "volume transmission," distinct from both tonic and classical synaptic transmission. Electrical connections are also notable in that, unlike other GABAergic cell types, neurogliaform family cells will form gap junctions not only with other neurogliaform cells, but also with non-neurogliaform family GABAergic cells. In this review, we focus on neurogliaform and Ivy cells throughout the hippocampal formation, where recent studies highlight their role in feedforward inhibition, uncover their ability to display a phenomenon called persistent firing, and reveal their modulation by opioids. The unique properties of this family of cells, their abundance, rich connectivity, and modulation by clinically relevant drugs make them an attractive target for future studies in vivo during different behavioral and pharmacological conditions.
Keywords: GABAA,slow; GABAB; feedforward inhibition; opioid; persistent firing.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ivy and neurogliaform interneurons are a major target of μ-opioid receptor modulation.J Neurosci. 2011 Oct 19;31(42):14861-70. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2269-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22016519 Free PMC article.
-
Gap-junctional coupling between neurogliaform cells and various interneuron types in the neocortex.J Neurosci. 2005 Jul 6;25(27):6278-85. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1431-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16000617 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis of ivy cells of the hippocampal CA1 stratum radiatum using spectral identification of immunofluorophores.Front Neural Circuits. 2012 May 31;6:35. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2012.00035. eCollection 2012. Front Neural Circuits. 2012. PMID: 22666191 Free PMC article.
-
Do GABAA and GABAB inhibitory postsynaptic responses originate from distinct interneurons in the hippocampus?Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1997 May;75(5):520-5. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9250387 Review.
-
GABAB receptors: modulation of thalamocortical dynamics and synaptic plasticity.Neuroscience. 2021 Feb 21;456:131-142. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.03.011. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Neuroscience. 2021. PMID: 32194227 Review.
Cited by
-
Development, Diversity, and Death of MGE-Derived Cortical Interneurons.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 27;22(17):9297. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179297. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experience-Dependent Regulation of Cajal-Retzius Cell Networks in the Developing and Adult Mouse Hippocampus.Cereb Cortex. 2018 Feb 1;28(2):672-687. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhx153. Cereb Cortex. 2018. PMID: 28637318 Free PMC article.
-
Postsynaptic dopamine D3 receptors selectively modulate μ-opioid receptor-expressing GABAergic inputs onto CA1 pyramidal cells in the rat ventral hippocampus.J Neurophysiol. 2024 Dec 1;132(6):2002-2011. doi: 10.1152/jn.00353.2024. Epub 2024 Nov 21. J Neurophysiol. 2024. PMID: 39570291
-
Quantitative assessment of CA1 local circuits: knowledge base for interneuron-pyramidal cell connectivity.Hippocampus. 2013 Sep;23(9):751-85. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22141. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Hippocampus. 2013. PMID: 23674373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurogliaform Cells Exhibit Laminar-specific Responses in the Visual Cortex and Modulate Behavioral State-dependent Cortical Activity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 11:2024.06.05.597539. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.05.597539. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38895403 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

