Relationships between total and allergen-specific serum IgE concentrations and lung function in young adults
- PMID: 22626596
- PMCID: PMC3956048
- DOI: 10.1016/j.anai.2012.04.008
Relationships between total and allergen-specific serum IgE concentrations and lung function in young adults
Abstract
Background: Prior studies have shown relationships between serum immunoglobulin E (IgE) and asthma.
Objective: To investigate relationships between total and allergen-specific IgE concentrations and lung function in young adults.
Methods: Measurements of total IgE, allergen-specific IgE to 6 common allergens, and spirometry (forced expiratory volume in one second [FEV(1)], forced vital capacity [FVC], FEV(1)/FVC, and percent change in FEV(1) after bronchodilation) were used to calculate correlations between the logarithmically transformed IgE values and measures of lung function among participants in a birth cohort not selected for risk of allergic disease stratified by current asthma, prior asthma, or no asthma.
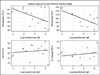
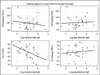
Results: The 428 participants were 51.6% female, 93% white, and 18.4 (standard deviation = 0.6) years old. Forty-eight (11.2%) had current asthma, 55 (12.9%) had a history of asthma, and 325 (75.9%) never had asthma. For males with current asthma, correlations between total IgE and FEV(1)% and FVC% were -0.51 (P = .06) and -0.70 (P = .005), respectively. For females with current asthma, the only significant correlation was between total IgE and the FEV(1)/FVC ratio (-0.55, P = .001). After excluding smokers and individuals without detectable allergen-specific IgE, the negative correlations for both males and females remained statistically significant. The correlations among males or females with prior asthma or no history of asthma were minimal and not statistically significant. The sum of the allergen-specific IgEs showed the same pattern of relationships to lung function as did total IgE.
Conclusion: Our results show significant negative correlations that vary by gender between both total and allergen-specific IgE and measurements of lung function in young adults with current asthma.
Copyright © 2012 American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any real or potential conflicts of interest with any of the information presented in the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlation between inhalant allergen-specific IgE and pulmonary function in children with asthma.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2005 Feb;39(2):150-5. doi: 10.1002/ppul.20163. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2005. PMID: 15633201
-
Relation of lung function and current inhalant allergen-specific immunoglobulin E concentrations in adolescents (GINIplus cohort).Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015 Sep;115(3):183-90. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2015.06.016. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26195441
-
Allergy, total serum immunoglobulin E, and airflow in children and adolescents in TENOR.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010 Dec;21(8):1157-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.2010.01065.x. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20444153
-
Association of elevated plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 levels with diminished lung function in patients with asthma.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011 May;106(5):371-7. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2010.12.021. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21530867 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between serum total IgE and disease severity in patients with allergic asthma in Spain.J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2015;25(2):120-7. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25997305
Cited by
-
Lung function in young adulthood: differences between males and females with asthma.ERJ Open Res. 2022 Jun 20;8(2):00154-2022. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00154-2022. eCollection 2022 Apr. ERJ Open Res. 2022. PMID: 35747229 Free PMC article.
-
Breastfeeding associated with higher lung function in African American youths with asthma.J Asthma. 2017 Oct;54(8):856-865. doi: 10.1080/02770903.2016.1266496. Epub 2016 Dec 8. J Asthma. 2017. PMID: 27929698 Free PMC article.
-
Total IgE plasma levels vary according to gender and age in Brazilian patients with allergic rhinitis.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2014 Nov;69(11):740-4. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2014(11)06. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2014. PMID: 25518031 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burrows B, Martinez FD, Halonen M, Barbee RA, Cline MG. Association of asthma with serum IgE levels and skin-test reactivity to allergens. N Engl J Med. 1989;320:271–277. - PubMed
-
- Sears MR, Burrows B, Flannery EM, Herbison GP, Hewitt CJ, Holdaway MD. Relation between airway responsiveness and serum IgE in children with asthma and in apparently normal children. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:1067–1071. - PubMed
-
- Vollmer WM, Buist AS, Johnson LR, McCamant LE, Halonen M. Relationship between serum IgE and cross-sectional and longitudinal FEV1 in two cohort studies. Chest. 1986;90:416–423. - PubMed
-
- Grunstein MM, Hakonarson H, Leiter J, et al. IL-13-dependent autocrine signaling mediates altered responsiveness of IgE-sensitized airway smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002;282(3):L520–L528. - PubMed

