Normal and pathologic concentrations of uremic toxins
- PMID: 22626821
- PMCID: PMC3380651
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2011121175
Normal and pathologic concentrations of uremic toxins
Erratum in
- J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013 Dec;24(12):2127-9
Abstract
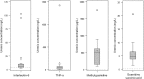
An updated review of the existing knowledge regarding uremic toxins facilitates the design of experimental studies. We performed a literature search and found 621 articles about uremic toxicity published after a 2003 review of this topic. Eighty-seven records provided serum or blood measurements of one or more solutes in patients with CKD. These records described 32 previously known uremic toxins and 56 newly reported solutes. The articles most frequently reported concentrations of β2-microglobulin, indoxyl sulfate, homocysteine, uric acid, and parathyroid hormone. We found most solutes (59%) in only one report. Compared with previous results, more recent articles reported higher uremic concentrations of many solutes, including carboxymethyllysine, cystatin C, and parathyroid hormone. However, five solutes had uremic concentrations less than 10% of the originally reported values. Furthermore, the uremic concentrations of four solutes did not exceed their respective normal concentrations, although they had been previously described as uremic retention solutes. In summary, this review extends the classification of uremic retention solutes and their normal and uremic concentrations, and it should aid the design of experiments to study the biologic effects of these solutes in CKD.
Figures

References
-
- Vanholder R, De Smet R, Glorieux G, Argilés A, Baurmeister U, Brunet P, Clark W, Cohen G, De Deyn PP, Deppisch R, Descamps-Latscha B, Henle T, Jörres A, Lemke HD, Massy ZA, Passlick-Deetjen J, Rodriguez M, Stegmayr B, Stenvinkel P, Tetta C, Wanner C, Zidek W, European Uremic Toxin Work Group (EUTox) : Review on uremic toxins: Classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int 63: 1934–1943, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Meert N, Schepers E, De Smet R, Argiles A, Cohen G, Deppisch R, Drüeke T, Massy Z, Spasovski G, Stegmayr B, Zidek W, Jankowski J, Vanholder R: Inconsistency of reported uremic toxin concentrations. Artif Organs 31: 600–611, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Vanholder R, Meert N, Schepers E, Glorieux G, Argiles A, Brunet P, Cohen G, Drüeke T, Mischak H, Spasovski G, Massy Z, Jankowski J, European Uremic Toxin Work Group (EUTox) : Review on uraemic solutes II—variability in reported concentrations: causes and consequences. Nephrol Dial Transplant 22: 3115–3121, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

