Skull metastasis as initial manifestation of pulmonary epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma: a case report of an unusual case
- PMID: 22629483
- PMCID: PMC3352177
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/610383
Skull metastasis as initial manifestation of pulmonary epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma: a case report of an unusual case
Abstract
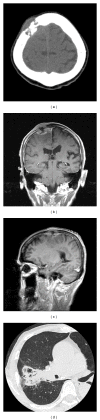
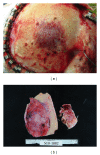
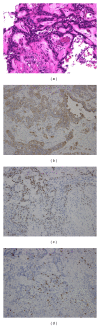
Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma (EMC) of the lung is rare and is considered to be low-grade malignancy. Intracranial metastasis of pulmonary EMC has not previously been reported according to our search of the literature. We report a case of skull metastasis as the initial manifestation of pulmonary EMC. An 81-year-old man complained of left leg motor weakness. Neurological examination showed left hemiparesis. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging revealed an osteolytic tumor in the right frontal bone with invasion to the dura and subdural space, attached to the superior sagittal sinus. Subtotal removal of the tumor was performed, and the left hemiparesis showed improvement. Histopathological study revealed the tumor to consist of epithelial and myoepithelial cells. Pulmonary EMC was diagnosed. The MIB-1 index in primary lesion was approximately 10%. The skull and dura are possible sites for metastasis from pulmonary EMC. The MIB-1 index is a predictive marker of malignant potential.
Figures
References
-
- Muslimani AA, Kundranda M, Jain S, Daw HA. Recurrent bronchial epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma after local therapy. Clinical Lung Cancer. 2007;8(6):386–388. - PubMed
-
- Doganay L, Bilgi S, Ozdil A, Yoruk Y, Altaner S, Kutlu K. Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma of the lung: a case report and review of the literature. Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine. 2003;127(4):e177–180. - PubMed
-
- Ruska A, Kerekes Z, Hovorková E, Bartoň P. Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma of the bronchus. Pathology Research and Practice. 1998;194(6):431–435. - PubMed
-
- Wilson RW, Moran CA. Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma of the lung: immunohistochemical and ultrastructural observations and review of the literature. Human Pathology. 1997;28(5):631–635. - PubMed
-
- Kang DY, Yoon YS, Kim HK, et al. Primary salivary gland-type lung cancer: surgical outcomes. Lung Cancer. 2010;72:250–254. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

