Data visualization in the neurosciences: overcoming the curse of dimensionality
- PMID: 22632718
- PMCID: PMC4427844
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.05.001
Data visualization in the neurosciences: overcoming the curse of dimensionality
Abstract
In publications, presentations, and popular media, scientific results are predominantly communicated through graphs. But are these figures clear and honest or misleading? We examine current practices in data visualization and discuss improvements, advocating design choices which reveal data rather than hide it.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
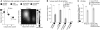
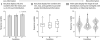
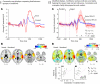
References
-
- Buckner RL, Andrews-Hanna JR, Schacter DL. The brain's default network: Anatomy, function, and relevance to disease. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2008;1124:1–38. - PubMed
-
- Cleveland WS. Graphs in scientific publications. American Statistician. 1984;38:261–269.
-
- Cleveland WS, McGill R. Graphical perception and graphical methods for analyzing scientific data. Science. 1985;229:828–833. - PubMed
-
- Cumming G, Finch S. Inference by eye: confidence intervals and how to read pictures of data. American Psychologist. 2005;60:170–180. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

