How we feel: ion channel partnerships that detect mechanical inputs and give rise to touch and pain perception
- PMID: 22632719
- PMCID: PMC3371091
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.04.023
How we feel: ion channel partnerships that detect mechanical inputs and give rise to touch and pain perception
Abstract
Every moment of every day, our skin and its embedded sensory neurons are bombarded with mechanical cues that we experience as pleasant or painful. Knowing the difference between innocuous and noxious mechanical stimuli is critical for survival and relies on the function of mechanoreceptor neurons that vary in their size, shape, and sensitivity. Their function is poorly understood at the molecular level. This review emphasizes the importance of integrating analysis at the molecular and cellular levels and focuses on the discovery of ion channel proteins coexpressed in the mechanoreceptors of worms, flies, and mice.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
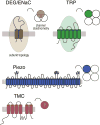
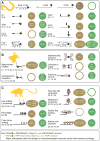
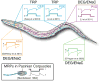

Similar articles
-
Piezo2 voltage-block regulates mechanical pain sensitivity.Brain. 2024 Oct 3;147(10):3487-3500. doi: 10.1093/brain/awae227. Brain. 2024. PMID: 38984717 Free PMC article.
-
TRPC1 contributes to light-touch sensation and mechanical responses in low-threshold cutaneous sensory neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2012 Feb;107(3):913-22. doi: 10.1152/jn.00658.2011. Epub 2011 Nov 9. J Neurophysiol. 2012. PMID: 22072513 Free PMC article.
-
PKCγ interneurons, a gateway to pathological pain in the dorsal horn.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2020 Apr;127(4):527-540. doi: 10.1007/s00702-020-02162-6. Epub 2020 Feb 27. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2020. PMID: 32108249 Review.
-
The DRASIC cation channel contributes to the detection of cutaneous touch and acid stimuli in mice.Neuron. 2001 Dec 20;32(6):1071-83. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00547-5. Neuron. 2001. PMID: 11754838
-
Transduction and encoding sensory information by skin mechanoreceptors.Pflugers Arch. 2015 Jan;467(1):109-19. doi: 10.1007/s00424-014-1651-7. Epub 2014 Nov 23. Pflugers Arch. 2015. PMID: 25416542 Review.
Cited by
-
Runx1 controls terminal morphology and mechanosensitivity of VGLUT3-expressing C-mechanoreceptors.J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 16;33(3):870-82. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3942-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23325226 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into DEG/ENaC channel gating from genetics and structure.Physiology (Bethesda). 2012 Oct;27(5):282-90. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00006.2012. Physiology (Bethesda). 2012. PMID: 23026751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A TRP channel trio mediates acute noxious heat sensing.Nature. 2018 Mar 29;555(7698):662-666. doi: 10.1038/nature26137. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29539642
-
Stomatin-domain protein interactions with acid-sensing ion channels modulate nociceptor mechanosensitivity.J Physiol. 2013 Nov 15;591(22):5555-74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.261180. Epub 2013 Aug 19. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23959680 Free PMC article.
-
The topographical attenuation of cutaneous input is modulated at the ankle joint during gait.Exp Brain Res. 2024 Jan;242(1):149-161. doi: 10.1007/s00221-023-06737-z. Epub 2023 Nov 18. Exp Brain Res. 2024. PMID: 37979067
References
-
- Akopian AN, Chen CC, Ding Y, Cesare P, Wood JN. A new member of the acid-sensing ion channel family. Neuroreport. 2000;11:2217–2222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

