LINC complexes form by binding of three KASH peptides to domain interfaces of trimeric SUN proteins
- PMID: 22632968
- PMCID: PMC3383001
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.046
LINC complexes form by binding of three KASH peptides to domain interfaces of trimeric SUN proteins
Abstract
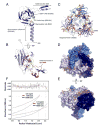
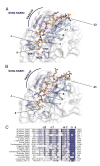
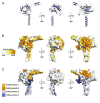
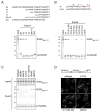
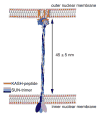
Linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton (LINC) complexes span the nuclear envelope and are composed of KASH and SUN proteins residing in the outer and inner nuclear membrane, respectively. LINC formation relies on direct binding of KASH and SUN in the perinuclear space. Thereby, molecular tethers are formed that can transmit forces for chromosome movements, nuclear migration, and anchorage. We present crystal structures of the human SUN2-KASH1/2 complex, the core of the LINC complex. The SUN2 domain is rigidly attached to a trimeric coiled coil that prepositions it to bind three KASH peptides. The peptides bind in three deep and expansive grooves formed between adjacent SUN domains, effectively acting as molecular glue. In addition, a disulfide between conserved cysteines on SUN and KASH covalently links both proteins. The structure provides the basis of LINC complex formation and suggests a model for how LINC complexes might arrange into higher-order clusters to enhance force-coupling.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
It takes KASH to hitch to the SUN.Cell. 2012 May 25;149(5):961-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.004. Cell. 2012. PMID: 22632963 No abstract available.
References
-
- Apel ED, Lewis RM, Grady RM, Sanes JR. Syne-1, a dystrophin- and Klarsicht-related protein associated with synaptic nuclei at the neuromuscular junction. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:31986–31995. - PubMed
-
- Appenzeller-Herzog C, Ellgaard L. The human PDI family: versatility packed into a single fold. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1783:535–548. - PubMed
-
- Bianchet MA, Odom EW, Vasta GR, Amzel LM. A novel fucose recognition fold involved in innate immunity. Nat Struct Biol. 2002;9:628–634. - PubMed
-
- Burke B, Roux KJ. Nuclei take a position: managing nuclear location. Dev Cell. 2009;17:587–597. - PubMed
-
- Chikashige Y, Tsutsumi C, Yamane M, Okamasa K, Haraguchi T, Hiraoka Y. Meiotic proteins bqt1 and bqt2 tether telomeres to form the bouquet arrangement of chromosomes. Cell. 2006;125:59–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

