Direct observation of the interconversion of normal and toxic forms of α-synuclein
- PMID: 22632969
- PMCID: PMC3383996
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.037
Direct observation of the interconversion of normal and toxic forms of α-synuclein
Abstract
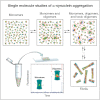
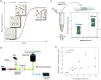
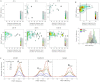
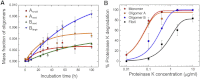
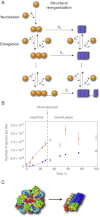
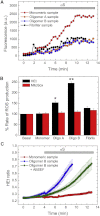
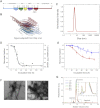
Here, we use single-molecule techniques to study the aggregation of α-synuclein, the protein whose misfolding and deposition is associated with Parkinson's disease. We identify a conformational change from the initially formed oligomers to stable, more compact proteinase-K-resistant oligomers as the key step that leads ultimately to fibril formation. The oligomers formed as a result of the structural conversion generate much higher levels of oxidative stress in rat primary neurons than do the oligomers formed initially, showing that they are more damaging to cells. The structural conversion is remarkably slow, indicating a high kinetic barrier for the conversion and suggesting that there is a significant period of time for the cellular protective machinery to operate and potentially for therapeutic intervention, prior to the onset of cellular damage. In the absence of added soluble protein, the assembly process is reversed and fibrils disaggregate to form stable oligomers, hence acting as a source of cytotoxic species.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

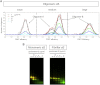
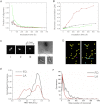
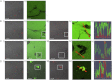
Comment in
-
Single-molecule approach to find out toxic oligomeric alpha-synuclein species formation.Mov Disord. 2012 Oct;27(12):1493. doi: 10.1002/mds.25180. Mov Disord. 2012. PMID: 23460945 No abstract available.
References
-
- Abeliovich A., Schmitz Y., Fariñas I., Choi-Lundberg D., Ho W.H., Castillo P.E., Shinsky N., Verdugo J.M., Armanini M., Ryan A. Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron. 2000;25:239–252. - PubMed
-
- Apetri M.M., Maiti N.C., Zagorski M.G., Carey P.R., Anderson V.E. Secondary structure of alpha-synuclein oligomers: characterization by raman and atomic force microscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 2006;355:63–71. - PubMed
-
- Balch W.E., Morimoto R.I., Dillin A., Kelly J.W. Adapting proteostasis for disease intervention. Science. 2008;319:916–919. - PubMed
-
- Bolognesi B., Kumita J.R., Barros T.P., Esbjorner E.K., Luheshi L.M., Crowther D.C., Wilson M.R., Dobson C.M., Favrin G., Yerbury J.J. ANS binding reveals common features of cytotoxic amyloid species. ACS Chem. Biol. 2010;5:735–740. - PubMed
-
- Bonini N.M., Giasson B.I. Snaring the function of alpha-synuclein. Cell. 2005;123:359–361. - PubMed
Supplemental References
-
- Orte, A., Clarke, R., Balasubramanian, S., and Klenerman, D. (2006). Determination of the fraction and stoichiometry of femtomolar levels of biomolecular complexes in an excess of monomer using single-molecule, two-color coincidence detection. Anal. Chem. 78, 7707–7715. - PubMed
-
- Panchuk-Voloshina, N., Haugland, R.P., Bishop-Stewart, J., Bhalgat, M.K., Millard, P.J., Mao, F., Leung, W.Y., and Haugland, R.P. (1999). Alexa dyes, a series of new fluorescent dyes that yield exceptionally bright, photostable conjugates. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 47, 1179–1188. - PubMed
-
- Uversky, V.N., Li, J., and Fink, A.L. (2001). Evidence for a partially folded intermediate in alpha-synuclein fibril formation. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 10737–10744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

