Ca(V)1 and Ca(V)2 channels engage distinct modes of Ca(2+) signaling to control CREB-dependent gene expression
- PMID: 22632974
- PMCID: PMC3654514
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.041
Ca(V)1 and Ca(V)2 channels engage distinct modes of Ca(2+) signaling to control CREB-dependent gene expression
Abstract
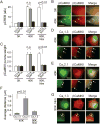
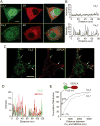
Activity-dependent gene expression triggered by Ca(2+) entry into neurons is critical for learning and memory, but whether specific sources of Ca(2+) act distinctly or merely supply Ca(2+) to a common pool remains uncertain. Here, we report that both signaling modes coexist and pertain to Ca(V)1 and Ca(V)2 channels, respectively, coupling membrane depolarization to CREB phosphorylation and gene expression. Ca(V)1 channels are advantaged in their voltage-dependent gating and use nanodomain Ca(2+) to drive local CaMKII aggregation and trigger communication with the nucleus. In contrast, Ca(V)2 channels must elevate [Ca(2+)](i) microns away and promote CaMKII aggregation at Ca(V)1 channels. Consequently, Ca(V)2 channels are ~10-fold less effective in signaling to the nucleus than are Ca(V)1 channels for the same bulk [Ca(2+)](i) increase. Furthermore, Ca(V)2-mediated Ca(2+) rises are preferentially curbed by uptake into the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. This source-biased buffering limits the spatial spread of Ca(2+), further attenuating Ca(V)2-mediated gene expression.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


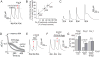


Similar articles
-
Exploring the dominant role of Cav1 channels in signalling to the nucleus.Biosci Rep. 2012 Dec 20;33(1):97-101. doi: 10.1042/BSR20120099. Biosci Rep. 2012. PMID: 23088728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired spatial learning related with decreased expression of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIalpha and cAMP-response element binding protein in the pentylenetetrazol-kindled rats.Brain Res. 2008 Oct 31;1238:108-17. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.07.103. Epub 2008 Aug 6. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18710651
-
Neuronal L-Type Calcium Channel Signaling to the Nucleus Requires a Novel CaMKIIα-Shank3 Interaction.J Neurosci. 2020 Mar 4;40(10):2000-2014. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0893-19.2020. Epub 2020 Feb 4. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32019829 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mechanism for Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II targeting to L-type Ca2+ channels that initiates long-range signaling to the nucleus.J Biol Chem. 2017 Oct 20;292(42):17324-17336. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.788331. Epub 2017 Sep 15. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28916724 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Ca(V)2 calcium channels by G protein coupled receptors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jul;1828(7):1629-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.10.004. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23063655 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome-Wide Profiling of Nascent RNA in Neurons with Enriched H3K27ac Signal Elevates eRNA Identification Efficiency.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024 Oct 8;15(20):3626-39. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00047. Online ahead of print. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39377285 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-dependent compensation of cell size is vulnerable to targeted deletion of ion channels.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 29;10(1):15989. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72977-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32994529 Free PMC article.
-
A membrane-delimited N-myristoylated CRMP2 peptide aptamer inhibits CaV2.2 trafficking and reverses inflammatory and postoperative pain behaviors.Pain. 2015 Jul;156(7):1247-1264. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000147. Pain. 2015. PMID: 25782368 Free PMC article.
-
CyclinD2-mediated regulation of neurogenic output from the retinal ciliary margin is perturbed in albinism.Neuron. 2023 Jan 4;111(1):49-64.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.10.025. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Neuron. 2023. PMID: 36351424 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Electrical Stimulation and the Modulation of the Axon Regeneration Program.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Aug 18;8:736. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00736. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33015031 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams JP, Dudek SM. Late-phase long-term potentiation: getting to the nucleus. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:737–743. - PubMed
-
- Alonso MT, Manjarres IM, Garcia-Sancho J. Modulation of calcium signalling by intracellular organelles seen with targeted aequorins. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2009;195:37–49. - PubMed
-
- Babcock DF, Hille B. Mitochondrial oversight of cellular Ca2+ signaling. Current opinion in neurobiology. 1998;8:398–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

