Interaction of pseudolaric acid B with the colchicine site of tubulin
- PMID: 22634405
- PMCID: PMC3402633
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.05.014
Interaction of pseudolaric acid B with the colchicine site of tubulin
Abstract
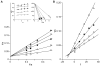
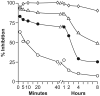
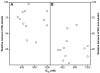
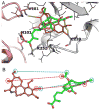
We purified pseudolaric acid B (PAB) from the root and stem bark of Pseudolarix kaempferi (Lindl.) Gorden. Confirming previous findings, we found that the compound had high nanomolar IC₅₀ antiproliferative effects in several cultured cell lines, causing mitotic arrest and the disappearance of intracellular microtubules. PAB strongly inhibited tubulin assembly (IC₅₀, 1.1 μM) but weakly inhibited the binding of colchicine to tubulin, as demonstrated by fluorescence and with [³H]colchicine. Kinetic analysis demonstrated that the mechanism of inhibition was competitive, with an apparent K(i) of 12-15 μM. Indirect studies demonstrated that PAB bound rapidly to tubulin and dissociated more rapidly from tubulin than the colchicine analog 2-methoxy-5-(2',3',4'-trimethoxyphenyl)tropone, whose complex with tubulin is known to have a half-life of 17s at 37 °C. We modeled PAB into the colchicine site of tubulin, using the crystal structure 1SA0 that contains two αβ-tubulin heterodimers, both bound to a colchicinoid and to a stathmin fragment. The binding model of PAB revealed common pharmacophoric features between PAB and colchicinoids, not readily apparent from their chemical structures.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
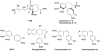

References
-
- Hamel E. An overview of compounds that interact with tubulin and their effects on microtubule assembly. In: Fojo AT, editor. Microtubule targets in cancer therapy. Totowa, New Jersey: Humana Press; 2008. pp. 1–20.pp. 2008
-
- Wong VKW, Chiu P, Chung SSM, Chow LMC, Zhao YZ, Yang BB, Ko BCB. Pseudolaric acid B, a novel microtubule-destabilizing agent that circumvents multidrug resistance phenotype and exhibits antitumor activity in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:6002–11. - PubMed
-
- Tong YG, Zhang XW, Geng MY, Yue JM, Xin XL, Tian F, Shen X, Tong LJ, Zhang C, Li WH, Lin LP, Ding LP. Pseudolarix Acid B, a new tubulin-binding agent, inhibits angiogenesis by interacting with a novel binding site on tubulin. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;69:1226–33. - PubMed
-
- Ravelli RBG, Gigant B, Curmi PA, Jourdain I, Lachkar S, Sobel A, Knossow M. Insight into tubulin regulation from a complex with colchicine and a stathmin-like domain. Nature. 2004;428:198–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

