A color-coding amacrine cell may provide a blue-off signal in a mammalian retina
- PMID: 22634731
- PMCID: PMC3386466
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3128
A color-coding amacrine cell may provide a blue-off signal in a mammalian retina
Abstract
Retinal amacrine cells are thought to lack chromatic or color-selective light responses and have only a minor role in color processing. We found that a type of mammalian (Ictidomys tridecemlineatus) amacrine cell selectively carries a blue-On signal, which is received from a blue or short wavelength-sensitive (S) cone On bipolar cell. This glycinergic inhibitory S-cone amacrine cell is ideally placed for driving blue-Off responses in downstream ganglion cells.
Figures
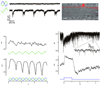

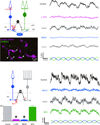
Comment in
-
Sensory systems: Inverting the blues.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012 Jun 20;13(7):450. doi: 10.1038/nrn3288. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22714013 No abstract available.
-
Another blue neuron in the retina.Nat Neurosci. 2012 Jun 26;15(7):930-1. doi: 10.1038/nn.3146. Nat Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22735511 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

