Mutations in the PCNA-binding domain of CDKN1C cause IMAGe syndrome
- PMID: 22634751
- PMCID: PMC3386373
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2275
Mutations in the PCNA-binding domain of CDKN1C cause IMAGe syndrome
Abstract
IMAGe syndrome (intrauterine growth restriction, metaphyseal dysplasia, adrenal hypoplasia congenita and genital anomalies) is an undergrowth developmental disorder with life-threatening consequences. An identity-by-descent analysis in a family with IMAGe syndrome identified a 17.2-Mb locus on chromosome 11p15 that segregated in the affected family members. Targeted exon array capture of the disease locus, followed by high-throughput genomic sequencing and validation by dideoxy sequencing, identified missense mutations in the imprinted gene CDKN1C (also known as P57KIP2) in two familial and four unrelated patients. A familial analysis showed an imprinted mode of inheritance in which only maternal transmission of the mutation resulted in IMAGe syndrome. CDKN1C inhibits cell-cycle progression, and we found that targeted expression of IMAGe-associated CDKN1C mutations in Drosophila caused severe eye growth defects compared to wild-type CDKN1C, suggesting a gain-of-function mechanism. All IMAGe-associated mutations clustered in the PCNA-binding domain of CDKN1C and resulted in loss of PCNA binding, distinguishing them from the mutations of CDKN1C that cause Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, an overgrowth syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
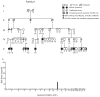

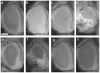


Comment in
-
Gain of function in CDKN1C.Nat Genet. 2012 Jun 27;44(7):737-8. doi: 10.1038/ng.2336. Nat Genet. 2012. PMID: 22735584 No abstract available.
References
-
- Vilain E, et al. IMAGe, a new clinical association of intrauterine growth retardation, metaphyseal dysplasia, adrenal hypoplasia congenita, and genital anomalies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999;84:4335–4340. - PubMed
-
- Bergada I, et al. Familial occurrence of the IMAGe association: additional clinical variants and a proposed mode of inheritance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:3186–3190. - PubMed
-
- Lee MH, Reynisdottir I, Massague J. Cloning of p57KIP2, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with unique domain structure and tissue distribution. Genes Dev. 1995;9:639–649. - PubMed
-
- Romanelli V, et al. CDKN1C (p57(Kip2)) analysis in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS) patients: Genotype-phenotype correlations, novel mutations, and polymorphisms. Am J Med Genet A. 2010;152A:1390–1397. - PubMed
-
- Hutz JE, et al. IMAGe association and congenital adrenal hypoplasia: no disease-causing mutations found in the ACD gene. Mol Genet Metab. 2006;88:66–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

