Toll-like receptor 3 plays a central role in cardiac dysfunction during polymicrobial sepsis
- PMID: 22635047
- PMCID: PMC3647525
- DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182535aeb
Toll-like receptor 3 plays a central role in cardiac dysfunction during polymicrobial sepsis
Abstract
Objective: To determine the role of Toll-like receptor 3 in cardiac dysfunction during polymicrobial sepsis.
Design: Controlled animal study.
Setting: University research laboratory.
Subjects: Male C57BL/6, wild-type, Toll-like receptor 3-/-.
Intervention: Myocardial dysfunction is a major consequence of septic shock and contributes to the high mortality of sepsis. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) play a critical role in the pathophysiology of sepsis/septic shock. TLR3 is located in intracellular endosomes, and recognizes double-stranded RNA. This study examined the role of TLR3 in cardiac dysfunction following cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced sepsis. TLR3 knockout (TLR3-/-, n=12) and age-matched wild-type (n=12) mice were subjected to CLP. Cardiac function was measured by echocardiography before and 6 hrs after CLP.
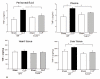
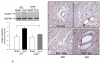
Measurements and main results: CLP resulted in significant cardiac dysfunction as evidenced by decreased ejection fraction by 25.7% and fractional shortening by 29.8%, respectively. However, TLR3-/- mice showed a maintenance of cardiac function at pre-CLP levels. Wild-type mice showed 50% mortality at 58 hrs and 100% mortality at 154 hrs after CLP. In striking contrast, 70% of TLR3-/- mice survived indefinitely, that is, >200 hrs. TLR3 deficiency significantly decreased CLP-induced cardiac-myocyte apoptosis and attenuated CLP-induced Fas and Fas ligand expression in the myocardium. CLP-activation of TLR4-mediated nuclear factor-κB and Toll/IL-1 receptor-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β-dependant interferon signaling pathways was prevented by TLR3 deficiency. In addition, CLP-increased vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression, and neutrophil and macrophage sequestration in the myocardium were also attenuated in septic TLR3-/- mice. More significantly, adoptive transfer of wild-type bone-marrow stromal cells to TLR3-/- mice abolished the cardioprotective effect in sepsis.
Conclusions: These data indicate that TLR3 plays a deleterious role in mediating cardiac dysfunction in sepsis. Thus, modulation of the TLR3 activity may be useful in preventing cardiac dysfunction in sepsis.
Figures

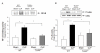
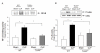
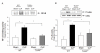
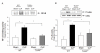
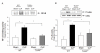









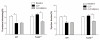
Comment in
-
Not only a toll for viruses: the role of toll-like receptor 3 in nonviral sepsis-induced cardiac depression.Crit Care Med. 2012 Aug;40(8):2514-5. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e318258e7b5. Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22809930 No abstract available.
References
-
- Krishnagopalan S, Kumar A, Parrillo JE, Kumar A. Myocardial dysfunction in the patient with sepsis. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2002;8:376–388. - PubMed
-
- Oberholzer A, Oberholzer C, Moldawer LL. Sepsis Syndromes: Understanding the Role of Innate and Acquired Immunity. Shock. 2001;16:83–96. - PubMed
-
- Aderem A, Ulevitch RJ. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature. 2000;406:782–787. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-Like Receptor Signalling. Nature Reviews. 2004;4:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Frantz S, Ertl G, Bauersachs J. Mechanisms of disease: Toll-like receptors in cardiovascular disease. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2007;4:444–454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

