Upregulation of plasmid genes during stationary phase in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803, a cyanobacterium
- PMID: 22636001
- PMCID: PMC3416404
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01174-12
Upregulation of plasmid genes during stationary phase in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803, a cyanobacterium
Erratum in
-
Correction for Berla and Pakrasi, Upregulation of Plasmid Genes during Stationary Phase in Synechocystis sp. Strain PCC 6803, a Cyanobacterium.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016 Sep 30;82(20):6291. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02273-16. Print 2016 Oct 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27694565 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
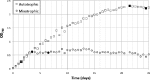
We analyzed DNA microarrays to identify highly expressed genes during stationary-phase growth of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Many identified genes are on endogenous plasmids, with copy numbers between 0.4 and 7 per chromosome. The promoters of such genes will be useful for synthetic biology applications with this phototrophic host.
Figures
References
-
- Cao Y, Xian M. 2011. Production of phloroglucinol by Escherichia coli using a stationary-phase promoter. Biotechnol. Lett. 33:1853–1858 - PubMed
-
- Foster J, Singh A, Rothschild L, Sherman L. 2007. Growth-phase dependent differential gene expression in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 and regulation by a group 2 sigma factor. Arch. Microbiol. 187:265–279 - PubMed
-
- Fu P. 2009. Genome-scale modeling of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and prediction of pathway insertion. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 84:473–483
-
- Gosse J, Engel B, Hui J, Harwood C, Flickinger M. 2010. Progress toward a biomimetic leaf: 4,000 h of hydrogen production by coating-stabilized nongrowing photosynthetic Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Biotechnol. Prog. 26:907–918 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources