High yield expression and purification of recombinant human apolipoprotein A-II in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 22636422
- PMCID: PMC3540857
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.D028043
High yield expression and purification of recombinant human apolipoprotein A-II in Escherichia coli
Abstract
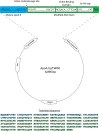
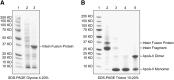
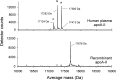
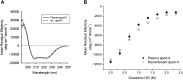
Recombinant expression systems have become powerful tools for understanding the structure and function of proteins, including the apolipoproteins that comprise human HDL. However, human apolipoprotein (apo)A-II has proven difficult to produce by recombinant techniques, likely contributing to our lack of knowledge about its structure, specific biological function, and role in cardiovascular disease. Here we present a novel Escherichia coli-based recombinant expression system that produces highly pure mature human apoA-II at substantial yields. A Mxe GyrA intein containing a chitin binding domain was fused at the C terminus of apoA-II. A 6× histidine-tag was also added at the fusion protein's C terminus. After rapid purification on a chitin column, intein auto-cleavage was induced under reducing conditions, releasing a peptide with only one extra N-terminal Met compared with the sequence of human mature apoA-II. A pass through a nickel chelating column removed any histidine-tagged residual fusion protein, leaving highly pure apoA-II. A variety of electrophoretic, mass spectrometric, and spectrophotometric analyses demonstrated that the recombinant form is comparable in structure to human plasma apoA-II. Similarly, recombinant apoA-II is comparable to the plasma form in its ability to bind and reorganize lipid and promote cholesterol efflux from macrophages via the ATP binding cassette transporter A1. This system is ideal for producing large quantities of recombinant wild-type or mutant apoA-II for structural or functional studies.
Figures
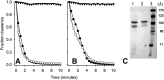
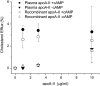
Similar articles
-
Purification and characterization of recombinant human apolipoprotein A-II expressed in Escherichia coli.Eur J Biochem. 1994 Nov 1;225(3):1141-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.1141b.x. Eur J Biochem. 1994. PMID: 7957205
-
Expression of the C-terminal domain of human apolipoprotein A-I using a chimeric apolipoprotein.Protein Expr Purif. 2017 Sep;137:13-19. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2017.06.008. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Protein Expr Purif. 2017. PMID: 28624493 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial expression and characterization of mature apolipoprotein A-I.Protein Expr Purif. 2002 Jul;25(2):353-61. doi: 10.1016/s1046-5928(02)00020-7. Protein Expr Purif. 2002. PMID: 12135571
-
Role of the Arg123-Tyr166 paired helix of apolipoprotein A-I in lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase activation.J Biol Chem. 1997 Jun 20;272(25):15967-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.25.15967. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9188498
-
Targeted expression, purification, and cleavage of fusion proteins from inclusion bodies in Escherichia coli.FEBS Lett. 2014 Jan 21;588(2):247-52. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.09.028. Epub 2013 Sep 27. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24076468 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential usefulness of apolipoprotein A2 isoforms for screening and risk stratification of pancreatic cancer.Biomark Med. 2016 Nov;10(11):1197-1207. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2016-0209. Epub 2016 Sep 27. Biomark Med. 2016. PMID: 27673558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High Efficient Expression, Purification, and Functional Characterization of Native Human Epidermal Growth Factor in Escherichia coli.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:3758941. doi: 10.1155/2016/3758941. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27766259 Free PMC article.
-
Purification of bacteriophage lambda repressor.Protein Expr Purif. 2013 Sep;91(1):30-6. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2013.06.013. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Protein Expr Purif. 2013. PMID: 23831434 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and purification of recombinant human apolipoprotein A-II in Pichia pastoris.Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2013 Oct;11(8):501-7. doi: 10.1089/adt.2013.511. Epub 2013 Oct 12. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2013. PMID: 24116940 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma biomarker for detection of early stage pancreatic cancer and risk factors for pancreatic malignancy using antibodies for apolipoprotein-AII isoforms.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 9;5:15921. doi: 10.1038/srep15921. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26549697 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gordon T., Castelli W. P., Hjortland M. C., Kannel W. B., Dawber T. R. 1977. High density lipoprotein as a protective factor against coronary heart disease. The Framingham Study. Am. J. Med. 62: 707–714 - PubMed
-
- Assmann G., Schulte H., von Eckardstein A., Huang Y. 1996. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol as a predictor of coronary heart disease risk. The PROCAM experience and pathophysiological implications for reverse cholesterol transport. Atherosclerosis. 124(Suppl): S11–S20 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

