Metabolism of circulating ADP in the bloodstream is mediated via integrated actions of soluble adenylate kinase-1 and NTPDase1/CD39 activities
- PMID: 22637533
- PMCID: PMC3425827
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.12-205658
Metabolism of circulating ADP in the bloodstream is mediated via integrated actions of soluble adenylate kinase-1 and NTPDase1/CD39 activities
Abstract
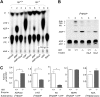
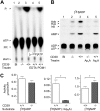
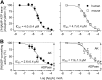
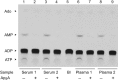
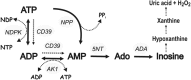
Extracellular ATP and ADP trigger inflammatory, vasodilatatory, and prothrombotic signaling events in the vasculature, and their turnover is governed by networks of membrane-associated enzymes. The contribution of soluble activities to intravascular nucleotide homeostasis remains controversial. By using thin-layer chromatographic assays, we revealed transphosphorylation of [γ-(32)P]ATP and AMP by human and murine sera, which was progressively inhibited by specific adenylate kinase (AK) inhibitor Ap(5)A. This phosphotransfer reaction was diminished markedly in serum from knockout mice lacking the major AK isoform, AK1, and in human serum immunodepleted of AK1. We also showed that ∼75% ADP in cell-free serum is metabolized via reversible AK1 reaction 2ADP ↔ ATP + AMP. The generated ATP and AMP are then metabolized through the coupled nucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase and 5'-nucleotidase/CD73 reactions, respectively. Constitutive presence of another nucleotide-converting enzyme, nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-1 (NTPDase1, known as CD39), was ascertained by the relative deficiency of serum from CD39-null mice to dephosphorylate [(3)H]ADP and [γ-(32)P]ATP, and also by diminished [(3)H]ADP hydrolysis by human serum pretreated with NTPDase1 inhibitors, POM-1 and ARL-67156. In summary, we have identified hitherto unrecognized soluble forms of AK1 and NTPDase1/CD39 that contribute in the active cycling between the principal platelet-recruiting agent ADP and other circulating nucleotides.
Figures
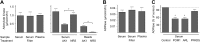
References
-
- Ralevic V., Burnstock G. (1998) Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol. Rev. 50, 413–492 - PubMed
-
- Marcus A. J., Broekman M. J., Drosopoulos J. H., Islam N., Pinsky D. J., Sesti C., Levi R. (2003) Metabolic control of excessive extracellular nucleotide accumulation by CD39/ecto-nucleotidase-1: implications for ischemic vascular diseases. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 305, 9–16 - PubMed
-
- Mercier N., Kiviniemi T. O., Saraste A., Miiluniemi M., Silvola J., Jalkanen S., Yegutkin G. G. (2012) Impaired ATP-induced coronary blood flow and diminished aortic NTPDase activity precede lesion formation in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Am. J. Pathol. 180, 419–428 - PubMed
-
- Yegutkin G. G. (2008) Nucleotide- and nucleoside-converting ectoenzymes: important modulators of purinergic signalling cascade. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1783, 673–694 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

