Lecithin:retinol acyltransferase is critical for cellular uptake of vitamin A from serum retinol-binding protein
- PMID: 22637576
- PMCID: PMC3397848
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.353979
Lecithin:retinol acyltransferase is critical for cellular uptake of vitamin A from serum retinol-binding protein
Abstract
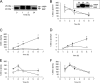
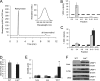
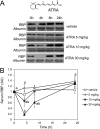
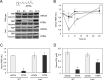
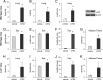
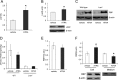
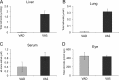
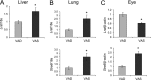
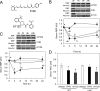
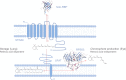
Vitamin A (all-trans-retinol) must be adequately distributed within the mammalian body to produce visual chromophore in the eyes and all-trans-retinoic acid in other tissues. Vitamin A is transported in the blood bound to retinol-binding protein (holo-RBP), and its target cells express an RBP receptor encoded by the Stra6 (stimulated by retinoic acid 6) gene. Here we show in mice that cellular uptake of vitamin A from holo-RBP depends on functional coupling of STRA6 with intracellular lecithin:retinol acyltransferase (LRAT). Thus, vitamin A uptake from recombinant holo-RBP exhibited by wild type mice was impaired in Lrat(-/-) mice. We further provide evidence that vitamin A uptake is regulated by all-trans-retinoic acid in non-ocular tissues of mice. When in excess, vitamin A was rapidly taken up and converted to its inert ester form in peripheral tissues, such as lung, whereas in vitamin A deficiency, ocular retinoid uptake was favored. Finally, we show that the drug fenretinide, used clinically to presumably lower blood RBP levels and thus decrease circulating retinol, targets the functional coupling of STRA6 and LRAT to increase cellular vitamin A uptake in peripheral tissues. These studies provide mechanistic insights into how vitamin A is distributed to peripheral tissues in a regulated manner and identify LRAT as a critical component of this process.
Figures
References
-
- Chambon P. (1996) A decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. FASEB J. 10, 940–954 - PubMed
-
- Paik J., Vogel S., Quadro L., Piantedosi R., Gottesman M., Lai K., Hamberger L., Vieira Mde M., Blaner W. S. (2004) Vitamin A. Overlapping delivery pathways to tissues from the circulation. J. Nutr. 134, 276S–280S - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

