Apolipoprotein E4 effects in Alzheimer's disease are mediated by synaptotoxic oligomeric amyloid-β
- PMID: 22637583
- PMCID: PMC3381721
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/aws127
Apolipoprotein E4 effects in Alzheimer's disease are mediated by synaptotoxic oligomeric amyloid-β
Abstract
The apolipoprotein E ε4 gene is the most important genetic risk factor for sporadic Alzheimer's disease, but the link between this gene and neurodegeneration remains unclear. Using array tomography, we analysed >50000 synapses in brains of 11 patients with Alzheimer's disease and five non-demented control subjects and found that synapse loss around senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease correlates with the burden of oligomeric amyloid-β in the neuropil and that this synaptotoxic oligomerized peptide is present at a subset of synapses. Further analysis reveals apolipoprotein E ε4 patients with Alzheimer's disease have significantly higher oligomeric amyloid-β burden and exacerbated synapse loss around plaques compared with apolipoprotein E ε3 patients. Apolipoprotein E4 protein colocalizes with oligomeric amyloid-β and enhances synaptic localization of oligomeric amyloid-β by >5-fold. Biochemical characterization shows that the amyloid-β enriched at synapses by apolipoprotein E4 includes sodium dodecyl sulphate-stable dimers and trimers. In mouse primary neuronal culture, lipidated apolipoprotein E4 enhances oligomeric amyloid-β association with synapses via a mechanism involving apolipoprotein E receptors. Together, these data suggest that apolipoprotein E4 is a co-factor that enhances the toxicity of oligomeric amyloid-β both by increasing its levels and directing it to synapses, providing a link between apolipoprotein E ε4 genotype and synapse loss, a major correlate of cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease.
Figures
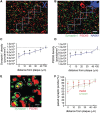
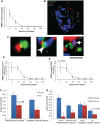
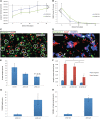
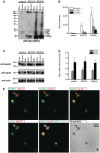


Comment in
-
Neurodegenerative disease: Insights into synaptotoxicity in AD.Nat Rev Neurol. 2012 Jun 19;8(7):357. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2012.121. Nat Rev Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22710622 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bellosta S, Nathan BP, Orth M, Dong LM, Mahley RW, Pitas RE. Stable expression and secretion of apolipoproteins E3 and E4 in mouse neuroblastoma cells produces differential effects on neurite outgrowth. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27063–71. - PubMed
-
- Chartier-Harlin MC, Parfitt M, Legrain S, Perez-Tur J, Brousseau T, Evans A, et al. Apolipoprotein E, epsilon 4 allele as a major risk factor for sporadic early and late-onset forms of Alzheimer's disease: analysis of the 19q13.2 chromosomal region. Hum Mol Genet. 1994;3:569–74. - PubMed
-
- Cleary JP, Walsh DM, Hofmeister JJ, Shankar GM, Kuskowski MA, Selkoe DJ, et al. Natural oligomers of the amyloid-beta protein specifically disrupt cognitive function. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:79–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

