Tracing epithelial stem cells during development, homeostasis, and repair
- PMID: 22641343
- PMCID: PMC3365500
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201201041
Tracing epithelial stem cells during development, homeostasis, and repair
Abstract
Epithelia ensure many critical functions of the body, including protection against the external environment, nutrition, respiration, and reproduction. Stem cells (SCs) located in the various epithelia ensure the homeostasis and repair of these tissues throughout the lifetime of the animal. Genetic lineage tracing in mice has allowed the labeling of SCs and their progeny. This technique has been instrumental in characterizing the origin and heterogeneity of epithelial SCs, their tissue location, and their differentiation potential under physiological conditions and during tissue regeneration.
Figures
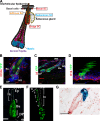
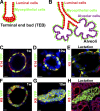
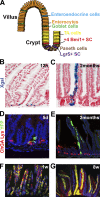
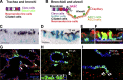
References
-
- Adamson I.Y., Bowden D.H. 1975. Derivation of type 1 epithelium from type 2 cells in the developing rat lung. Lab. Invest. 32:736–745 - PubMed
-
- Barker N., Huch M., Kujala P., van de Wetering M., Snippert H.J., van Es J.H., Sato T., Stange D.E., Begthel H., van den Born M., et al. 2010b. Lgr5(+ve) stem cells drive self-renewal in the stomach and build long-lived gastric units in vitro. Cell Stem Cell. 6:25–36 10.1016/j.stem.2009.11.013 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

