Programmed cell death 1 forms negative costimulatory microclusters that directly inhibit T cell receptor signaling by recruiting phosphatase SHP2
- PMID: 22641383
- PMCID: PMC3371732
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20112741
Programmed cell death 1 forms negative costimulatory microclusters that directly inhibit T cell receptor signaling by recruiting phosphatase SHP2
Abstract
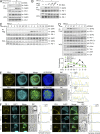
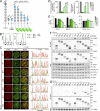
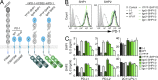
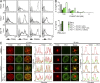
Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) is a negative costimulatory receptor critical for the suppression of T cell activation in vitro and in vivo. Single cell imaging elucidated a molecular mechanism of PD-1-mediated suppression. PD-1 becomes clustered with T cell receptors (TCRs) upon binding to its ligand PD-L1 and is transiently associated with the phosphatase SHP2 (Src homology 2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase 2). These negative costimulatory microclusters induce the dephosphorylation of the proximal TCR signaling molecules. This results in the suppression of T cell activation and blockade of the TCR-induced stop signal. In addition to PD-1 clustering, PD-1-TCR colocalization within microclusters is required for efficient PD-1-mediated suppression. This inhibitory mechanism also functions in PD-1(hi) T cells generated in vivo and can be overridden by a neutralizing anti-PD-L1 antibody. Therefore, PD-1 microcluster formation is important for regulation of T cell activation.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

