Approach to infants born at 22 to 24 weeks' gestation: relationship to outcomes of more-mature infants
- PMID: 22641761
- PMCID: PMC3362905
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2011-2216
Approach to infants born at 22 to 24 weeks' gestation: relationship to outcomes of more-mature infants
Abstract
Objective: We sought to determine if a center's approach to care of premature infants at the youngest gestational ages (22-24 weeks' gestation) is associated with clinical outcomes among infants of older gestational ages (25-27 weeks' gestation).
Methods: Inborn infants of 401 to 1000 g birth weight and 22 0/7 to 27 6/7 weeks' gestation at birth from 2002 to 2008 were enrolled into a prospectively collected database at 20 centers participating in the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Markers of an aggressive approach to care for 22- to 24-week infants included use of antenatal corticosteroids, cesarean delivery, and resuscitation. The primary outcome was death before postnatal day 120 for infants of 25 to 27 weeks' gestation. Secondary outcomes were the combined outcomes of death or a number of morbidities associated with prematurity.
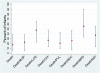
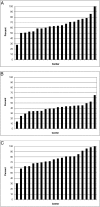
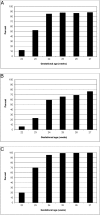
Results: Our study included 3631 infants 22 to 24 weeks' gestation and 5227 infants 25 to 27 weeks' gestation. Among the 22- to 24-week infants, use of antenatal corticosteroids ranged from 28% to 100%, cesarean delivery from 13% to 65%, and resuscitation from 30% to 100% by center. Centers with higher rates of antenatal corticosteroid use in 22- to 24-week infants had reduced rates of death, death or retinopathy of prematurity, death or late-onset sepsis, death or necrotizing enterocolitis, and death or neurodevelopmental impairment in 25- to 27-week infants.
Conclusions: This study suggests that physicians' willingness to provide care to extremely low gestation infants as measured by frequency of use of antenatal corticosteroids is associated with improved outcomes for more-mature infants.
Figures
References
-
- Vohr BR, Wright LL, Dusick AM, et al. Neonatal Research Network Center differences and outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 2004;113(4):781–789 - PubMed
-
- Halm EA, Lee C, Chassin MR. Is volume related to outcome in health care? A systematic review and methodologic critique of the literature. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137(6):511–520 - PubMed
-
- Birkmeyer JD, Stukel TA, Siewers AE, Goodney PP, Wennberg DE, Lucas FL. Surgeon volume and operative mortality in the United States. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(22):2117–2127 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 HD060040/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025764/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053119/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024160/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1K23HD060040-01/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 5U10 HD040492-10/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DHHS-1R18AE000028-01/AE/ASPE HHS/United States
- U10 HD040498/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 2RRHD057713-02/PHS HHS/United States
- U10 HD053124/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040521/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053109/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR008084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001449/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD053089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040461/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000041/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR007122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD036790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR006022/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

