Telmisartan directly ameliorates the neuronal inflammatory response to IL-1β partly through the JNK/c-Jun and NADPH oxidase pathways
- PMID: 22642771
- PMCID: PMC3410820
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-102
Telmisartan directly ameliorates the neuronal inflammatory response to IL-1β partly through the JNK/c-Jun and NADPH oxidase pathways
Abstract
Background: Blockade of angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptors ameliorates brain inflammation, and reduces excessive brain interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) production and release from cortical microglia. The aim of this study was to determine whether, in addition, AT1 receptor blockade directly attenuates IL-1β-induced inflammatory responses in neuronal cultures.
Methods: SK-N-SH human neuroblasts and primary rat cortical neurons were pretreated with telmisartan followed by exposure to IL-1β. Gene expression was determined by reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR, protein expression and kinase activation by western blotting, NADPH oxidase activity by the lucigenin method, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) release by enzyme immunoassay, reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation by the dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate fluorescent probe assay, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) involvement was assessed with the antagonists GW9662 and T0070907, the agonist pioglitazone and the expression of PPARγ target genes ABCG1 and CD36.
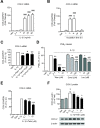
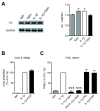
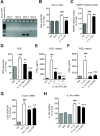
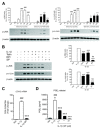
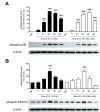
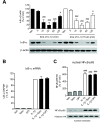
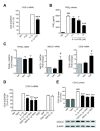
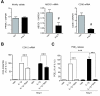
Results: We found that SK-N-SH neuroblasts expressed AT1 but not AT2 receptor mRNA. Telmisartan reduced IL-1β-induced cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression and PGE2 release more potently than did candesartan and losartan. Telmisartan reduced the IL-1β-induced increase in IL-1R1 receptor and NADPH oxidase-4 (NOX-4) mRNA expression, NADPH oxidase activity, and ROS generation, and reduced hydrogen peroxide-induced COX-2 gene expression. Telmisartan did not modify IL-1β-induced ERK1/2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation or nuclear factor-κB activation but significantly decreased IL-1β-induced c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and c-Jun activation. The JNK inhibitor SP600125 decreased IL-1β-induced PGE2 release with a potency similar to that of telmisartan. The PPARγ agonist pioglitazone reduced IL-1β-induced inflammatory reaction, whereas telmisartan did not activate PPARγ, as shown by its failure to enhance the expression of the PPARγ target genes ABCG1 and CD36, and the inability of the PPARγ antagonists GW9662 and T0070907 to modify the effect of telmisartan on COX-2 induction. The effect of telmisartan on IL-1β-stimulated COX-2 and IL-1R1 mRNA expression and ROS production was replicated in primary rat cortical neurons.
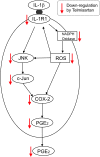
Conclusions: Telmisartan directly ameliorates IL-1β-induced neuronal inflammatory response by inhibition of oxidative stress and the JNK/c-Jun pathway. Our results support the hypothesis that AT1 receptor blockers are directly neuroprotective, and should be considered for the treatment of inflammatory conditions of the brain.
Figures
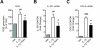
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

