The prevalence, patterns and predictors of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in a developing country
- PMID: 22642973
- PMCID: PMC3408375
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-5996-4-21
The prevalence, patterns and predictors of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in a developing country
Abstract
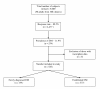
Prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) has reached epidemic proportions in Sri Lanka. Presently there are studies on the community prevalence of distal peripheral neuropathy (DPN) in Sri Lanka. We describe prevalence, patterns and predictors of DPN in patients with DM in Sri Lanka. Data were collected as part of a national study on DM. In new cases DPN was assessed using the Diabetic-Neuropathy-Symptom (DNS) score, while in those with established diabetes both DNS and Toronto-Clinical-Scoring-System (TCSS) were used. A binary logistic-regression analysis was performed with 'presence of DPN' as the dichomatous dependent variable and other independent co-variants. The study included 528 diabetic patients (191-new cases), with a mean age of 55.0 ± 12.4 years and 37.3% were males, while 18% were from urban areas. Prevalence of DPN according to DNS score among all patients, patients with already established diabetes and newly diagnosed patients were 48.1%, 59.1% and 28.8% respectively. Prevalence of DPN in those with established DM as assessed by TCSS was 24% and the majority had mild DPN (16.6%). The remainder of the abstract is based on subjects with established DM. The prevalence of DPN in males and female was 20.0% and 26.4% respectively. The mean age of those with and without DPN was 62.1 ± 10.8 and 55.1 ± 10.8 years respectively (p < 0.001). The majority of those with DPN were from rural-areas (75.3%) and earned a monthly income < Sri Lankan Rupees 12,000 (87.6%). In the binary logistic-regression presence of foot ulcers (OR:10.4; 95%CI 1.8-16.7), female gender (OR:6.7; 95%CI 2.0-9.8) and smoking (OR:5.9; 95%CI 1.4-9.7) were the strongest predictors followed by insulin treatment (OR:4.3; 95%CI 1.3-6.9), diabetic retinopathy (OR:2.7; 95%CI 1.3-5.4), treatment with sulphonylureas (OR:1.8; 95%CI 1.1-3.2), increasing height (OR:1.8; 95%CI 1.2-2.4), rural residence (OR:1.8; 95%CI 1.1-2.5), higher levels of triglycerides (OR:1.6; 95%CI 1.2-2.0) and longer duration of DM (OR:1.2; 95%CI 1.1-1.3). There is a high prevalence of DPN among Sri Lankan adults with diabetes. The study defines the impact of previously known risk factors for development of DPN and identifies several new potential risk factors in an ethnically different large subpopulation with DM.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott CA, Carrington AL, Ashe H, Bath S, Every LC, Griffiths J, Hann AW, Hussein A, Jackson N, Johnson KE. et al. The North-West Diabetes Foot Care Study: incidence of, and risk factors for, new diabetic foot ulceration in a community-based patient cohort. Diabet Med. 2002;19(5):377–384. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2002.00698.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association, American Academy of Neurology. Consensus statement: report and recommendations of the san antonio conference on diabetic neuropathy. american diabetes association american academy of neurology. Diabetes Care. 1988;11(7):592–597. - PubMed
-
- Melton LJI, Dyck PJ. Epidemiology: In Diabetic Neuropathy. 2 edition. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia; 1999.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources