A new immunoprecipitation-real time quantitative PCR assay for anti-Th/To and anti-U3RNP antibody detection in systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 22643159
- PMCID: PMC3446509
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3858
A new immunoprecipitation-real time quantitative PCR assay for anti-Th/To and anti-U3RNP antibody detection in systemic sclerosis
Abstract
Introduction: Classic anti-nucleolar antibodies anti-Th/To and U3 ribonucleoprotein (-U3RNP) can help in the diagnosis, prediction of organ involvement and prognosis in systemic sclerosis (SSc); however, no validated commercial assay is available. We aimed at establishing a novel quantitative real time PCR (qPCR) method to detect these antibodies.
Methods: Standard immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed using K562 cell extract and RNA components were extracted. cDNA was reverse transcribed from RNA components and Th RNA and U3 RNA were detected by qPCR using custom primers. Cycle threshold (Ct) values were compared in a titration experiment to determine the assay efficacy. The new assay was evaluated by testing 22 anti-Th/To and 12 anti-U3RNP positive samples in addition to 88 controls, and the results were compared with IP as a gold standard.
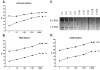
Results: By testing serial 1:8 dilutions of cell lysate as the substrate in the IP step, RNA extracted after IP, and its derived cDNA, linear dose response curves were noted for both anti-Th/To and -U3RNP. With every dilution, Ct values changed approximately three as expected, reflecting the eight-fold difference of cDNA. The Ct difference between positive and negative samples was 8 to 13, which was similar throughout the dilutions. In the specificity analysis, the Ct values of positive samples were clearly different from the negative groups and the results by qPCR had a near perfect correlation with IP.
Conclusions: Our new method readily detects these two clinically important antibodies in SSc. Making tests for anti-Th/To and -U3RNP antibodies widely available to clinicians should be helpful in the diagnosis and follow-up of SSc patients.
Figures

References
-
- Hamaguchi Y. Autoantibody profiles in systemic sclerosis: predictive value for clinical evaluation and prognosis. J Dermatol. 2010;37:42–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

