Acute compartment syndrome: obtaining diagnosis, providing treatment, and minimizing medicolegal risk
- PMID: 22644598
- PMCID: PMC3535085
- DOI: 10.1007/s12178-012-9126-y
Acute compartment syndrome: obtaining diagnosis, providing treatment, and minimizing medicolegal risk
Abstract
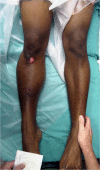
Acute compartment syndrome (ACS) is a surgical emergency. Diagnosis depends on a high clinical suspicion and an understanding of risk factors, pathophysiology and subtle physical exam findings. The typical high risk scenario for ACS is a male patient younger than 35 years of age, involved in a high energy sport or roadway collision, resulting in a tibial shaft fracture. He will go on to develop acute compartment syndrome of the leg in less than 10 hours and require emergent fasciotomy. Diagnosis of ACS in this patient is primarily a clinical one but can be confirmed with invasive intracompartmental pressure monitoring or non-invasive near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). Delaying the diagnosis will likely result in some degree of permanent disability and places the surgeon at high risk for litigation. This article reviews the salient features of acute compartment syndrome that should be understood by all orthopaedic residents and surgeons.
Figures
References
-
- McQueen MM, Christie J, Court-Brown CM. Compartment pressures after intramedullary nailing of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990;72:395–397. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources