Distinct functions of JNK and c-Jun in oxidant-induced hepatocyte death
- PMID: 22644775
- PMCID: PMC3636504
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.24203
Distinct functions of JNK and c-Jun in oxidant-induced hepatocyte death
Abstract
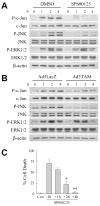
Overactivation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)/c-Jun signaling is a central mechanism of hepatocyte injury and death including that from oxidative stress. However, the functions of JNK and c-Jun are still unclear, and this pathway also inhibits hepatocyte death. Previous studies of menadione-induced oxidant stress demonstrated that toxicity resulted from sustained JNK/c-Jun activation as death was blocked by the c-Jun dominant negative TAM67. To further delineate the function of JNK/c-Jun signaling in hepatocyte injury from oxidant stress, the effects of direct JNK inhibition on menadione-induced death were examined. In contrast to the inhibitory effect of TAM67, pharmacological JNK inhibition by SP600125 sensitized the rat hepatocyte cell line RALA255-10G to death from menadione. SP600125 similarly sensitized mouse primary hepatocytes to menadione toxicity. Death from SP600125/menadione was c-Jun dependent as it was blocked by TAM67, but independent of c-Jun phosphorylation. Death occurred by apoptosis and necrosis and activation of the mitochondrial death pathway. Short hairpin RNA knockdowns of total JNK or JNK2 sensitized to death from menadione, whereas a jnk1 knockdown was protective. Jnk2 null mouse primary hepatocytes were also sensitized to menadione death. JNK inhibition magnified decreases in cellular ATP content and β-oxidation induced by menadione. This effect mediated cell death as chemical inhibition of β-oxidation also sensitized cells to death from menadione, and supplementation with the β-oxidation substrate oleate blocked death. Components of the JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway have opposing functions in hepatocyte oxidant stress with JNK2 mediating resistance to cell death and c-Jun promoting death.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
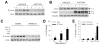
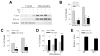
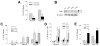
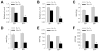
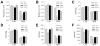
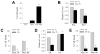
References
-
- Abdel-aleem S, Li X, Anstadt MP, Perez-Tamayo RA, Lowe JE. Regulation of glucose utilization during the inhibition of fatty acid oxidation in rat myocytes. Horm Metab Res. 1994;26:88–91. - PubMed
-
- Bradham CA, Hatano E, Brenner DA. Dominant-negative TAK1 induces c-Myc and G0 exit in liver. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001;281:G1279–G1289. - PubMed
-
- Brown PH, Alani R, Preis LH, Szabo E, Birrer MJ. Suppression of oncogene-induced transformation by a deletion mutant of c-jun. Oncogene. 1993;8:877–886. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

